Thoracic manifestations of IgG4-related disease
- PMID: 36437514
- PMCID: PMC10100266
- DOI: 10.1111/resp.14422
Thoracic manifestations of IgG4-related disease
Abstract
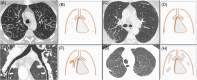
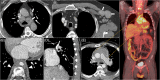
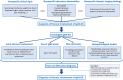
Immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a recently described rare systemic fibroinflammatory disease with an estimated incidence of less than 1 in 100,000 persons per year. The disease can affect virtually any organ and is characterized by unifying histopathological findings. Recently, four subgroups of patients have been characterized: hepatobiliary, head and neck, Mikulicz syndrome and retroperitoneal fibrosis, who illustrate the mainly abdominal and ENT tropism of the disease. Yet, thoracic involvement is not uncommon. It can be detected in up to 30% of patients with systemic IgG4-RD and is the exclusive manifestation of the disease in about 10% of cases. Clinical symptoms are nonspecific and may include dyspnoea, cough or chest pain. Chest CT findings are heterogeneous and primarily include peribronchovascular thickening, nodules, ground-glass opacities and lymphadenopathy. There is no specific diagnostic test for IgG4-RD thoracic involvement, which may mimic malignancy or vasculitis. Therefore, a cautious approach is needed to make an accurate diagnosis: a search for extra-thoracic manifestations, elevated serum IgG4 levels, circulating levels of plasmablasts and pathologic evidence of disease is warranted. Although very suggestive, neither the presence of a polyclonal IgG4 lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate, storiform fibrosis or obliterative phlebitis are sufficient to confirm the histological diagnosis. Steroids are recommended as first-line therapy. Rituximab or disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs may be used in relapsed or rare cases of steroid-refractory disease. In this review, we summarize current knowledge regarding the pathophysiology, epidemiology, diagnostic modalities (clinical-biological-imaging-histopathology) and treatment of IgG4-RD thoracic involvement.
Keywords: IgG4; immunoglobulin G4-related disease; interstitial lung disease; rare systemic fibroinflammatory disease; thoracic.
© 2022 The Authors. Respirology published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Asian Pacific Society of Respirology.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Stone JH, Zen Y, Deshpande V. IgG4‐related disease. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:539–51. - PubMed
-
- Sarles H, Sarles JC, Muratore R, Guien C. Chronic inflammatory sclerosis of the pancreas—an autonomous pancreatic disease? Am J Dig Dis. 1961;6:688–98. - PubMed
-
- Hamano H, Kawa S, Horiuchi A, Unno H, Furuya N, Akamatsu T, et al. High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:732–8. - PubMed
-
- Kamisawa T, Funata N, Hayashi Y, Eishi Y, Koike M, Tsuruta K, et al. A new clinicopathological entity of IgG4‐related autoimmune disease. J Gastroenterol. 2003;38:982–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

