A scoping review of pediatric microdialysis: A missed opportunity for microdialysis in the pediatric neuro-oncology setting
- PMID: 36438644
- PMCID: PMC9683385
- DOI: 10.1093/noajnl/vdac171
A scoping review of pediatric microdialysis: A missed opportunity for microdialysis in the pediatric neuro-oncology setting
Abstract
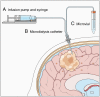
Background: Brain microdialysis is a minimally invasive technique for monitoring analytes, metabolites, drugs, neurotransmitters, and/or cytokines. Studies to date have centered on adults with traumatic brain injury, with a limited number of pediatric studies performed. This scoping review details past use of brain microdialysis in children and identifies potential use for future neuro-oncology trials.
Methods: In December 2020, Cochrane Library: CENTRAL, Embase, PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science: Core Collection were searched. Two reviewers screened all articles by title and abstract review and then full study texts, using microdialysis in patients less than 18 yo.
Results: Of the 1171 articles screened, 49 were included. The 49 studies included 472 pediatric patients (age range 0-17 years old), in the brain (21), abdominal (16), and musculoskeletal (12) regions. Intracerebral microdialysis was performed in 64 collective patients, with a median age of 11 years old, and predominance in metabolic evaluations.
Conclusion: Historically, pediatric microdialysis was safely performed within the brain in varied neurologic conditions, except neuro-oncology. Adult brain tumor studies using intratumoral/peritumoral microdialysis sampling can inform future pediatric studies to advance diagnosis and treatment options for such aggressive tumors.
Keywords: brain tumor; cancer; intracerebral monitoring; microdialysis; pediatric; pharmacokinetics.
Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Neuro-Oncology and the European Association of Neuro-Oncology 2022.
Figures
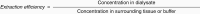
References
-
- Krebs-Kraft DL, Frantz KJ, Parent MB. In vivo microdialysis: a method for sampling extracellular fluid in discrete brain regions. In: Lajtha A, Baker G, Dunn S, Holt A, eds. Handbook of Neurochemistry and Molecular Neurobiology: Practical Neurochemistry Methods. US: Springer US; 2007:219–256.
-
- Carpenter KLH, Young AMH, Hutchinson PJ. Advanced monitoring in traumatic brain injury: microdialysis. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2017;23(2):103–109. - PubMed
-
- Reinstrup P, Mellergård P, Uski T. Intracerebral microdialysis in clinical practice: baseline values for chemical markers during wakefulness, anesthesia, and neurosurgery. Neurosurgery. 2000;47(3):701–709. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
