Association between dietary inflammation and erectile dysfunction among US adults: A cross-sectional analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2001-2004
- PMID: 36438746
- PMCID: PMC9691656
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2022.930272
Association between dietary inflammation and erectile dysfunction among US adults: A cross-sectional analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2001-2004
Abstract
Background: Although chronic low-grade inflammation has been linked to the development of erectile dysfunction (ED), the association between pro-inflammatory diets and ED is unclear. The dietary inflammation index (DII) is a novel method to quantify the inflammatory potential of a diet.
Objective: Our objective was to investigate the association between the DII and ED among US males.
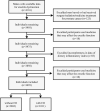
Design: This cross-sectional study included 3,693 males 20-85 year of age from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2001-2004. Multivariable-adjusted logistic regression models were used to assess the association between the DII and ED. All analyses accounted for the complex sampling design.
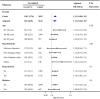
Results: The mean ± SE of the DII was 0.8 ± 0.1 and 0.4 ± 0.1 among participants with and without ED, respectively. After adjusting for age, race/ethnicity, education, smoking status, physical activity, drinking status, hypertension, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, hypercholesterolemia, BMI, and eGFR, the DII score was associated with ED (odds ratio 1.12; 95% CI: 1.04-1.19). Moreover, this association was also stable in our subgroup analysis or sensitivity analyses.
Conclusion: Dietary inflammatory potential, as estimated by the DII score, is positively associated with ED among US males.
Keywords: NHANES; cross-sectional study; dietary recall; dietary score; erectile dysfunction; inflammation.
Copyright © 2022 Ruan, Xie, Yu, Liu, Jing and Lu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Male and Female Sexual Function and Dysfunction; Andrology.J Urol. 2023 Jun;209(6):1218-1221. doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000003420. Epub 2023 Mar 22. J Urol. 2023. PMID: 36946106 No abstract available.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

