Emerging roles of selenium on metabolism and type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 36438755
- PMCID: PMC9686347
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1027629
Emerging roles of selenium on metabolism and type 2 diabetes
Abstract
Selenium is recognized as an essential element for human health and enters human body mainly via diet. Selenium is a key constituent in selenoproteins, which exert essential biological functions, including antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Several selenoproteins including glutathione peroxidases, selenoprotein P and selenoprotein S are known to play roles in the regulation of type 2 diabetes. Although there is a close association between certain selenoproteins with glucose metabolism or insulin resistance, the relationship between selenium and type 2 diabetes is complex and remains uncertain. Here we review recent advances in the field with an emphasis on roles of selenium on metabolism and type 2 diabetes. Understanding the association between selenium and type 2 diabetes is important for developing clinical practice guidelines, establishing and implementing effective public health policies, and ultimately combating relative health issues.
Keywords: dietary intake; glucose and lipid metabolism; selenium; selenoproteins; type 2 diabetes.
Copyright © 2022 Zhao, Zou, Huo, Wei and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
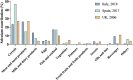

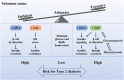
References
-
- Galan-Chilet I, Tellez-Plaza M, Guallar E, De Marco G, Lopez-Izquierdo R, Gonzalez-Manzano I, et al. Plasma selenium levels and oxidative stress biomarkers: a gene-environment interaction Population-Based study. Free Radic Biol Med. (2014) 74:229–36. 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.07.005 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

