Perception of educational environment with an assessment of motivational learning strategies and emotional intelligence as factors affecting medical students' academic achievement
- PMID: 36439015
- PMCID: PMC9683452
- DOI: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_1772_21
Perception of educational environment with an assessment of motivational learning strategies and emotional intelligence as factors affecting medical students' academic achievement
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to investigate how medical students perceive their educational environment, as well as the implications of motivation, learning strategies, and the factor of emotional intelligence on academic achievement.
Materials and methods: In a cross-sectional study, 3384 undergraduate students were recruited from randomly selected Egyptian medical colleges. Students from second to final year, taking fundamental and clinical courses and, at a minimum, three professional exams, were enrolled and subjected to the Dundee Ready Educational Environment Measure scale, the Motivated Strategies for Learning Questionnaire, and Emotional intelligence questionnaire.
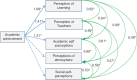
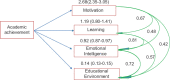
Results: The overall mean age of the studied students was 21.42 ± 1.61 years. Females represented 63.5%, rural residents were 52.2% and students with enough income represented 88.0%. The traditional system adopted 28.4% of the students versus 71.6% in the integrated system. Linear regression using path analysis was conducted to study the predictors of academic achievement, and it revealed that motivation was the highly significant predictor of academic achievement (β = 2.68, CI95%:2.35-3.05, P < 0.001), followed by learning (β = 1.09, CI95%:0.80-1.41, P < 0.001), emotional intelligence (β = 0.92, CI95%:0.87-0.97, P < 0.001), and the educational environment (β = 0.14, CI95%:0.13-0.15, P < 0.001).
Conclusion: The study's findings have implications for medical educators trying to understand the personal factors that influence learning and performance in medical school. Students' motivation was the highly significant predictor of academic achievement followed by learning, emotional intelligence, and educational environment. Perception of the learning environment had improved because of the integrated student-centered system, which fosters motivation and emotional intelligence. To improve learners' EI, optimal learning, and educational outcomes, the EI components can be taught and fostered.
Keywords: Academic achievement; educational environment; emotional intelligence; integrated teaching; learning strategies; medical education; motivation.
Copyright: © 2022 Journal of Education and Health Promotion.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Smith SR. Toward an integrated medical curriculum. Med Health R I. 2005;88:258–61. - PubMed
-
- Huber MT, Hutchings P. 2nd ed. Washington, DC: Association of American Colleges and Universities; 2009. Integrative Learning: Mapping the Terrain The Academy in Transition.
-
- Dent J, Harden RM, Hun D. 4th ed. Churchill Livingstone Elsevier Health Sciences. London, New York, Oxford, Philadelphia, St. Louis Sydney, Toronto: Medical CD Center Co. Ltd 9., Elsevier Limited; 2013. A Practical Guide for Medical Teachers.
-
- Badrawi N, HosnI S, Rashwan M. NatNational Academic Reference Standards (NARS): Medical (Draft) 2017. Available from: https://med.sohag-univ.edu.eg/main/wp-content/uploads/2020/02/NARS.pdf .
-
- Abdelaziz A, Kassab SE, Abdelnasser A, Hosny S. Medical education in Egypt: Historical background, current status, and challenges. Health Prof Educ. 2018;4:236–44.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

