NFIL3 and its immunoregulatory role in rheumatoid arthritis patients
- PMID: 36439145
- PMCID: PMC9692021
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.950144
NFIL3 and its immunoregulatory role in rheumatoid arthritis patients
Abstract
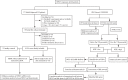
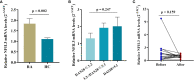
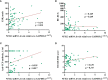
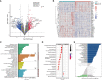
Nuclear-factor, interleukin 3 regulated (NFIL3) is an immune regulator that plays an essential role in autoimmune diseases. However, the relationship between rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and NFIL3 remains largely unknown. In this study, we examined NFIL3 expression in RA patients and its potential molecular mechanisms in RA. Increased NFIL3 expression levels were identified in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from 62 initially diagnosed RA patients and 75 healthy controls (HCs) by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR). No correlation between NFIL3 and disease activity was observed. In addition, NFIL3 expression was significantly upregulated in RA synovial tissues analyzed in the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) dataset (GSE89408). Then, we classified synovial tissues into NFIL3-high (≥75%) and NFIL3-low (≤25%) groups according to NFIL3 expression levels. Four hundred five differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between the NFIL3-high and NFIL3-low groups were screened out using the "limma" R package. Enrichment analysis showed that most of the enriched genes were primarily involved in the TNF signaling pathway via NFκB, IL-17 signaling pathway, and rheumatoid arthritis pathways. Then, 10 genes (IL6, IL1β, CXCL8, CCL2, PTGS2, MMP3, MMP1, FOS, SPP1, and ADIPOQ) were identified as hub genes, and most of them play a key role in RA. Positive correlations between the hub genes and NFIL3 were revealed by qRT-PCR in RA PBMCs. An NFIL3-related protein-protein interaction (PPI) network was constructed using the STRING database, and four clusters (mainly participating in the inflammatory response, lipid metabolism process, extracellular matrix organization, and circadian rhythm) were constructed with MCODE in Cytoscape. Furthermore, 29 DEGs overlapped with RA-related genes from the RADB database and were mainly enriched in IL-17 signaling pathways. Thus, our study revealed the elevated expression of NFIL3 in both RA peripheral blood and synovial tissues, and the high expression of NFIL3 correlated with the abnormal inflammatory cytokines and inflammatory responses, which potentially contributed to RA progression.
Keywords: GEO; NFIL3; bioinformatics analysis; immune regulation; rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Copyright © 2022 Du, Zheng, Chen, Wang, Pu, Yu, Yan, Chen, Wang, Shen, Li and Pan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Exploration and Identification of Potential Biomarkers and Immune Cell Infiltration Analysis in Synovial Tissue of Rheumatoid Arthritis.Int J Rheum Dis. 2025 Feb;28(2):e70137. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.70137. Int J Rheum Dis. 2025. PMID: 39953769
-
The expression of RBPJ and its potential role in rheumatoid arthritis.BMC Genomics. 2024 Sep 30;25(1):899. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10804-2. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39350019 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Disease-Specific Hub Biomarkers and Immune Infiltration in Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Tissues by Bioinformatics Analysis.Dis Markers. 2021 May 17;2021:9911184. doi: 10.1155/2021/9911184. eCollection 2021. Dis Markers. 2021. PMID: 34113405 Free PMC article.
-
A new border for circadian rhythm gene NFIL3 in diverse fields of cancer.Clin Transl Oncol. 2023 Jul;25(7):1940-1948. doi: 10.1007/s12094-023-03098-5. Epub 2023 Feb 15. Clin Transl Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36788184 Review.
-
Gene expression profiling meta-analysis reveals novel gene signatures and pathways shared between tuberculosis and rheumatoid arthritis.PLoS One. 2019 Mar 7;14(3):e0213470. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0213470. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30845171 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Disruption of the biorhythm in gastric epithelial cell triggers inflammation in Helicobacter pylori-associated gastritis by aberrantly regulating NFIL3 via CagA activated ERK-SP1 pathway.Cell Commun Signal. 2025 Jun 15;23(1):285. doi: 10.1186/s12964-025-02302-z. Cell Commun Signal. 2025. PMID: 40518541 Free PMC article.
-
A new prognostic model for RHOV, ABCC2, and CYP4B1 to predict the prognosis and association with immune infiltration of lung adenocarcinoma.J Thorac Dis. 2023 Apr 28;15(4):1919-1934. doi: 10.21037/jtd-23-265. Epub 2023 Apr 10. J Thorac Dis. 2023. PMID: 37197482 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Impact of the Gut Microbiota/REV-ERBα/NF-κB Axis on the Circadian Rhythmicity of Gout Flares from a Chronobiological Perspective.J Inflamm Res. 2025 Jun 19;18:8141-8151. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S525351. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 40551987 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NFIL3 contributes to cytotoxic T lymphocyte-mediated killing.Open Biol. 2024 Feb;14(2):230456. doi: 10.1098/rsob.230456. Epub 2024 Feb 28. Open Biol. 2024. PMID: 38412963 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic potential of Coptis chinensis for arthritis with underlying mechanisms.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Aug 11;14:1243820. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1243820. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37637408 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

