SKA1/2/3 is a biomarker of poor prognosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 36439516
- PMCID: PMC9684634
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1038925
SKA1/2/3 is a biomarker of poor prognosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Spindle and kinetochore-associated complex subunits 1-3 (SKA1-3) stabilize the kinetochore-attached spindle microtubules in metaphase. Due to the dysregulation in multiple cancers, SKA1-3 is considered a predictor for the prognosis of the patients. However, the potential clinical applications of SKA1-3, particularly in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) prognosis and progression, have completely unknown yet.
Methods: For the analysis of SKA1-3 expression and applications in clinics in HCC patients, several databases, such as STRING, UALCAN, GEO, and TCGA, were searched. In addition, the underlying mechanisms of SKA for the regulation of HCC occurrence, development, and progression were also explored.
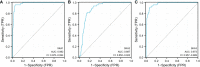
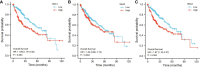
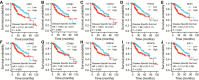
Results: Compared to the normal controls, HCC patients showed dramatically elevated SKA1-3 expression at the mRNA level, and the values of the area under the curve (AUC) were 0.982, 0.887, and 0.973, respectively. Increased SKA1-3 expression levels were associated with the clinical stage, age, body mass index, tumor grade, tissue subtype, and Tp53 mutation status in HCC patients. The analyses of Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genome (KEGG) and Gene ontology (GO) demonstrated that SKA1-3 are enriched mainly in the Fanconi anemia, homologous recombination, spliceosome, DNA replication, and cell cycle signaling pathways. The hub genes, such as CDK1, CCNB1, CCNA2, TOP2A, BUB1, AURKB, CCNB2, BUB1B, NCAPG, and KIF11, were identified in protein-protein interactions (PPIs). The expression levels of hub genes were increased in HCC patients and predictive of a poor prognosis. Finally, the expression levels of SKA1-3 were determined using the GEO database.
Conclusions: SKA1-3 are potential prognostic biomarkers of and targets for HCC. In addition, SKA1-3 may affect HCC prognosis via the Fanconi anemia pathway, homologous recombination, spliceosome, DNA replication, and cell cycle signaling pathway.
Keywords: bioinformatics analysis; biomarker; enrichment analysis; liver hepatocellular carcinoma; spindle and kinetochore-associated complex subunit (SKA).
Copyright © 2022 Song, He, Ji, Duan, Zhang and Hu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures









References
-
- Liu Z, Jiang Y, Yuan H, Fang Q, Cai N, Suo C, et al. . The trends in incidence of primary liver cancer caused by specific etiologies: Results from the global burden of disease study 2016 and implications for liver cancer prevention. J Hepatol (2019) 70:674–83. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.12.001 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lisoway AJ, Zai CC, Zai G, Nair A, Ebrahimi S, Tiwari AK, et al. . PT613. the role of SKA2 genetic and epigenetic variation in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol (2016) 19:25. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyw044.613 - DOI
-
- Boks MP, Rutten BPF, Geuze E, Houtepen LC, Vermetten E, Kaminsky Z, et al. . SKA2 methylation is involved in cortisol stress reactivity and predicts the development of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) after military deployment. Neuropsychopharmacol Off Publ Am Coll Neuropsychopharmacol (2016) 41:1350–6. doi: 10.1038/npp.2015.286 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

