Deuterated Drugs and Biomarkers in the COVID-19 Pandemic
- PMID: 36440130
- PMCID: PMC9685803
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.2c04160
Deuterated Drugs and Biomarkers in the COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
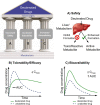
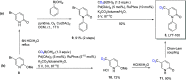
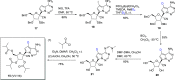
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a highly contagious disease caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Initially identified in Wuhan (China) in December 2019, COVID-19 rapidly spread globally, resulting in the COVID-19 pandemic. Carriers of the SARS-CoV-2 can experience symptoms ranging from mild to severe (or no symptoms whatsoever). Although vaccination provides extra immunity toward SARS-CoV-2, there has been an urgent need to develop treatments for COVID-19 to alleviate symptoms for carriers of the disease. In seeking a potential treatment, deuterated compounds have played a critical role either as therapeutic agents or as internal MS standards for studying the pharmacological properties of new drugs by quantifying the parent compounds and metabolites. We have identified >70 examples of deuterium-labeled compounds associated with treatment of COVID-19. Of these, we found 9 repurposed drugs and >20 novel drugs studied for potential therapeutic roles along with a total of 38 compounds (drugs, biomarkers, and lipids) explored as internal mass spectrometry standards. This review details the synthetic pathways and modes of action of these compounds (if known), and a brief analysis of each study.
© 2022 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): V.D. is an employee of Sanofi and may hold shares or options in the company. The other authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



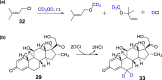
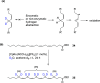


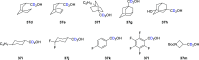
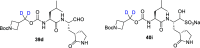
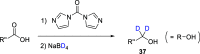
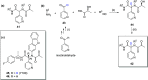



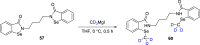
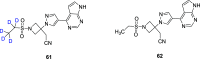


References
-
- Gordon D. E.; Jang G. M.; Bouhaddou M.; Xu J.; Obernier K.; White K. M.; O’Meara M. J.; Rezelj V. V.; Guo J. Z.; Swaney D. L.; Tummino T. A.; Huttenhain R.; Kaake R. M.; Richards A. L.; Tutuncuoglu B.; Foussard H.; Batra J.; Haas K.; Modak M.; Kim M.; Haas P.; Polacco B. J.; Braberg H.; Fabius J. M.; Eckhardt M.; Soucheray M.; Bennett M. J.; Cakir M.; McGregor M. J.; Li Q.; Meyer B.; Roesch F.; Vallet T.; Mac Kain A.; Miorin L.; Moreno E.; Naing Z. Z. C.; Zhou Y.; Peng S.; Shi Y.; Zhang Z.; Shen W.; Kirby I. T.; Melnyk J. E.; Chorba J. S.; Lou K.; Dai S. A.; Barrio-Hernandez I.; Memon D.; Hernandez-Armenta C.; Lyu J.; Mathy C. J. P.; Perica T.; Pilla K. B.; Ganesan S. J.; Saltzberg D. J.; Rakesh R.; Liu X.; Rosenthal S. B.; Calviello L.; Venkataramanan S.; Liboy-Lugo J.; Lin Y.; Huang X.-P.; Liu Y.; Wankowicz S. A.; Bohn M.; Safari M.; Ugur F. S.; Koh C.; Savar N. S.; Tran Q. D.; Shengjuler D.; Fletcher S. J.; O’Neal M. C.; Cai Y.; Chang J. C. J.; Broadhurst D. J.; Klippsten S.; Sharp P. P.; Wenzell N. A.; Kuzuoglu-Ozturk D.; Wang H.-Y.; Trenker R.; Young J. M.; Cavero D. A.; Hiatt J.; Roth T. L.; Rathore U.; Subramanian A.; Noack J.; Hubert M.; Stroud R. M.; Frankel A. D.; Rosenberg O. S.; Verba K. A.; Agard D. A.; Ott M.; Emerman M.; Jura N.; von Zastrow M.; Verdin E.; Ashworth A.; Schwartz O.; d’Enfert C.; Mukherjee S.; Jacobson M.; Malik H. S.; Fujimori D. G.; Ideker T.; Craik C. S.; Floor S. N.; Fraser J. S.; Gross J. D.; Sali A.; Roth B. L.; Ruggero D.; Taunton J.; Kortemme T.; Beltrao P.; Vignuzzi M.; Garcia-Sastre A.; Shokat K. M.; Shoichet B. K.; Krogan N. J. A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing. Nature 2020, 583 (7816), 459–468. 10.1038/s41586-020-2286-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Guy R. K.; DiPaola R. S.; Romanelli F.; Dutch R. E. Rapid repurposing of drugs for COVID-19. Science 2020, 368 (6493), 829–830. 10.1126/science.abb9332. - DOI - PubMed
- El Bairi K.; Trapani D.; Petrillo A.; Le Page C.; Zbakh H.; Daniele B.; Belbaraka R.; Curigliano G.; Afqir S. Repurposing anticancer drugs for the management of COVID-19. Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 141, 40–61. 10.1016/j.ejca.2020.09.014. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhang W.; Zhao Y.; Zhang F.; Wang Q.; Li T.; Liu Z.; Wang J.; Qin Y.; Zhang X.; Yan X.; Zeng X.; Zhang S. The use of anti-inflammatory drugs in the treatment of people with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): The perspectives of clinical immunologists from China. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 214, 108393.10.1016/j.clim.2020.108393. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Know Your Treatment Options for COVID-19; https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/know-your-treatment-optio... (accessed 2022–08–25).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

