Marine fungi showing multifunctional activity against human pathogenic microbes and cancer
- PMID: 36441723
- PMCID: PMC9704632
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0276926
Marine fungi showing multifunctional activity against human pathogenic microbes and cancer
Abstract
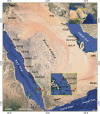
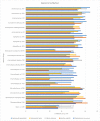
Multifunctional drugs have shown great promise in biomedicine. Organisms with antimicrobial and anticancer activity in combination with antioxidant activity need further research. The Red Sea and the Arabian Gulf coasts were randomly sampled to find fungi with multifunctional activity. One hundred strains (98 fungi and 2 lichenized forms) were isolated from 15 locations. One-third of the isolates inhibited clinical bacterial (Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis, Vibrio cholerae, Salmonella typhi, S. paratyphi) and fungal pathogens (Talaromycets marneffei, Malassezia globose, Cryptococcus neoformans, Candida albicans, Aspergillus fumigatus) and four cancer cell lines (Hep G2 liver, A-549 lung, A-431skin, MCF 7 breast cancer). Bacterial and cancer inhibition was often accompanied by a high antioxidant activity, as indicated by the principal component analysis (PCA). PCA also indicated that fungal and bacterial pathogens appeared to be inhibited mostly by different marine fungal isolates. Strains with multifunctional activity were found more from the Rea Sea than from the Arabian Gulf coasts. The highest potential for multifunctional drugs were observed for Acremonium sp., Acrocalymma sp., Acrocalymma africana, Acrocalymma medicaginis (activity reported for the first time), Aspergillus sp. Cladosporium oxysporum, Emericellopsis alkaline, Microdochium sp., and Phomopsis glabrae. Lung, skin, and breast cancers were inhibited 85%-97% by Acremonium sp, while most of the isolates showed low inhibition (ca 20%). The highest antifungal activity was observed for Acremonium sp., Diaporthe hubeiensis, Lasiodiplodia theobromae, and Nannizia gypsea. One Acremonium sp. is of particular interest to offer a multifunctional drug; it displayed both antifungal and antibacterial activity combined with high antioxidant activity (DPPH scavenging 97%). A. medicaginis displayed combined antibacterial, anticancer, and antioxidant activity being of high interest. Several genera and some species included strains with both high and low biological activities pointing out the need to study several isolates to find the most efficient strains for biomedical applications.
Copyright: © 2022 Ameen et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Liu L, Ma Q, Cao J, Gao Y, Han S, Liang Y, et al. Recent progress of graphene oxide-based multifunctional nanomaterials for cancer treatment. Cancer Nanotechnol. 2021;12: 1–31.
-
- Duan S, Wu R, Xiong Y-H, Ren H-M, Lei C, Zhao Y-Q, et al. Multifunctional antimicrobial materials: From rational design to biomedical applications. Prog Mater Sci. 2022;125: 100887.
-
- Rashad FM, Fathy HM, El-Zayat AS, Elghonaimy AM. Isolation and characterization of multifunctional Streptomyces species with antimicrobial, nematicidal and phytohormone activities from marine environments in Egypt. Microbiol Res. 2015;175: 34–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

