Molecular modelling of the HCMV IL-10 protein isoforms and analysis of their interaction with the human IL-10 receptor
- PMID: 36441804
- PMCID: PMC9704672
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0277953
Molecular modelling of the HCMV IL-10 protein isoforms and analysis of their interaction with the human IL-10 receptor
Erratum in
-
Correction: Molecular modelling of the HCMV IL-10 protein isoforms and analysis of their interaction with the human IL-10 receptor.PLoS One. 2023 Nov 30;18(11):e0295457. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0295457. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 38033121 Free PMC article.
Abstract
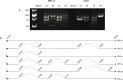
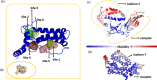
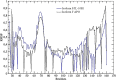
The human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) UL111A gene encodes several homologs of the cellular interleukin 10 (cIL-10). Alternative splicing in the UL111A region produces two relatively well-characterized transcripts designated cmvIL-10 (isoform A) and LAcmvIL-10 (isoform B). The cmvIL-10 protein is the best characterized, both structurally and functionally, and has many immunosuppressive activities similar to cIL-10, while LAcmvIL-10 has more restricted biological activities. Alternative splicing also results in five less studied UL111A transcripts encoding additional proteins homologous to cIL-10 (isoforms C to G). These transcripts were identified during productive HCMV infection of MRC-5 cells with the high passage laboratory adapted AD169 strain, and the structure and properties of the corresponding proteins are largely unknown. Moreover, it is unclear whether these protein isoforms are able to bind the cellular IL-10 receptor and induce signalling. In the present study, we investigated the expression spectrum of UL111A transcripts in fully permissive MRC-5 cells and semi permissive U251 cells infected with the low passage HCMV strain TB40E. We identified a new spliced transcript (H) expressed during productive infection. Using computational methods, we carried out molecular modelling studies on the three-dimensional structures of the HCMV IL-10 proteins encoded by the transcripts detected in our work (cmvIL-10 (A), LAcmvIL-10 (B), E, F and H) and on their interaction with the human IL-10 receptor (IL-10R1). The modelling predicts clear differences between the isoform structures. Furthermore, the in silico simulations (molecular dynamics simulation and normal-mode analyses) allowed us to evaluate regions that contain potential receptor binding sites in each isoform. The analyses demonstrate that the complexes between the isoforms and IL-10R1 present different types of molecular interactions and consequently different affinities and stabilities. The knowledge about structure and expression of specific viral IL-10 isoforms has implications for understanding of their properties and role in HCMV immune evasion and pathogenesis.
Copyright: © 2022 Pantaleão et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Expression Profile of Human Cytomegalovirus UL111A cmvIL-10 and LAcmvIL-10 Transcripts in Primary Cells and Cells from Renal Transplant Recipients.Viruses. 2025 Mar 31;17(4):501. doi: 10.3390/v17040501. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40284944 Free PMC article.
-
Human Cytomegalovirus Interleukin 10 Homologs: Facing the Immune System.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Jun 9;10:245. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00245. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32582563 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Latency-associated viral interleukin-10 (IL-10) encoded by human cytomegalovirus modulates cellular IL-10 and CCL8 Secretion during latent infection through changes in the cellular microRNA hsa-miR-92a.J Virol. 2014 Dec;88(24):13947-55. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02424-14. Epub 2014 Sep 24. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 25253336 Free PMC article.
-
Human Cytomegalovirus UL111A and US27 Gene Products Enhance the CXCL12/CXCR4 Signaling Axis via Distinct Mechanisms.J Virol. 2018 Feb 12;92(5):e01981-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01981-17. Print 2018 Mar 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29237840 Free PMC article.
-
[Interrelationship between human cytomegalovirus infection and chemokine].Nihon Rinsho. 1998 Jan;56(1):69-74. Nihon Rinsho. 1998. PMID: 9465667 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Is the vIL-10 Protein from Cytomegalovirus Associated with the Potential Development of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia?Viruses. 2025 Mar 18;17(3):435. doi: 10.3390/v17030435. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40143362 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Human Cytomegalovirus Latency-Associated Gene Product Latency Unique Natural Antigen Regulates Latent Gene Expression.Viruses. 2023 Sep 4;15(9):1875. doi: 10.3390/v15091875. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 37766281 Free PMC article.
-
Expression Profile of Human Cytomegalovirus UL111A cmvIL-10 and LAcmvIL-10 Transcripts in Primary Cells and Cells from Renal Transplant Recipients.Viruses. 2025 Mar 31;17(4):501. doi: 10.3390/v17040501. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40284944 Free PMC article.
-
Correction: Molecular modelling of the HCMV IL-10 protein isoforms and analysis of their interaction with the human IL-10 receptor.PLoS One. 2023 Nov 30;18(11):e0295457. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0295457. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 38033121 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

