Notes on demand: Conceptual and empirical benefits of applying Rachlin's discounting equation to demand data
- PMID: 36442017
- PMCID: PMC9852225
- DOI: 10.1037/adb0000889
Notes on demand: Conceptual and empirical benefits of applying Rachlin's discounting equation to demand data
Abstract
Objective: Howard Rachlin wrote extensively on how value diminishes in a hyperbolic form, and he contributed to understanding choice processes between different commodities as a molar pattern of behavior. The field of behavioral economic demand has been dominated by exponential decay functions, indicating that decreases in consumption of a commodity are best fit by exponential functions. Because of the success of Rachlin's equation at describing how hyperbolic decay affects the value of a commodity across various factors (e.g., delay, probability, social distance), we attempted to extend his equation to behavioral economic demand data for alcohol and opioids.
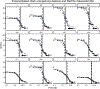
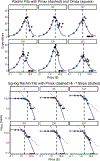
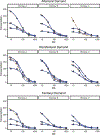
Method: Rachlin's discounting equation was applied to estimate consumption on alcohol purchase task data and nonhuman drug demand data. We compared results of his equation to the exponentiated demand equation using both a mixed-effects modeling approach and a two-stage approach.
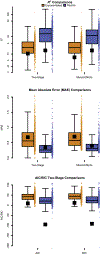
Results: Rachlin's equation provided better fits to consumption data than the exponentiated equation for both mixed-effects and two-stage modeling. We also found that traditional demand metrics, such as Pmax, can be derived analytically when using Rachlin's equation. Certain metrics derived from Rachlin's equation appeared to be related to clinical covariates in ways similar to the exponentiated equation.
Conclusions: Rachlin's equation better described demand data than did the exponentiated equation, indicating that demand for a commodity may decrease hyperbolically rather than exponentially. Other benefits of his equation are that it does not have the same pitfalls as the current exponential equations and is relatively straightforward in its conceptualization when applied to demand data. (PsycInfo Database Record (c) 2023 APA, all rights reserved).
Figures


Similar articles
-
Hyperbolic discounting and exponentiated demand: Modeling demand for cigarettes in three dimensions.J Exp Anal Behav. 2023 Jan;119(1):169-191. doi: 10.1002/jeab.818. Epub 2022 Dec 23. J Exp Anal Behav. 2023. PMID: 36562640 Free PMC article.
-
Howard Rachlin: An extended scientist.J Exp Anal Behav. 2023 Jan;119(1):16-24. doi: 10.1002/jeab.819. Epub 2022 Dec 14. J Exp Anal Behav. 2023. PMID: 36518021
-
Behavioral construction of the future.Psychol Addict Behav. 2023 Feb;37(1):13-24. doi: 10.1037/adb0000853. Epub 2022 Jun 27. Psychol Addict Behav. 2023. PMID: 35758981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rachlin's extended self: Influences on a Brazilian research group.J Exp Anal Behav. 2023 Jan;119(1):231-239. doi: 10.1002/jeab.809. Epub 2023 Jan 5. J Exp Anal Behav. 2023. PMID: 36602121
-
Utilizing the commodity purchase task to evaluate behavioral economic demand for illicit substances: a review and meta-analysis.Addiction. 2020 Mar;115(3):393-406. doi: 10.1111/add.14792. Epub 2019 Oct 16. Addiction. 2020. PMID: 31454109 Review.
Cited by
-
Overviewing the exponential model of demand and introducing a simplification that solves issues of span, scale, and zeros.Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2025 Apr;33(2):209-223. doi: 10.1037/pha0000754. Epub 2025 Feb 27. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40014511 Review.
-
Hyperbolic discounting and exponentiated demand: Modeling demand for cigarettes in three dimensions.J Exp Anal Behav. 2023 Jan;119(1):169-191. doi: 10.1002/jeab.818. Epub 2022 Dec 23. J Exp Anal Behav. 2023. PMID: 36562640 Free PMC article.

