Brain PET Imaging: Approach to Cognitive Impairment and Dementia
- PMID: 36442959
- PMCID: PMC9713600
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cpet.2022.09.006
Brain PET Imaging: Approach to Cognitive Impairment and Dementia
Erratum in
-
Erratum.PET Clin. 2023 Apr;18(2):xi. doi: 10.1016/j.cpet.2023.01.002. PET Clin. 2023. PMID: 36858749 No abstract available.
Abstract
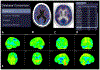
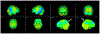
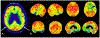
Alzheimer disease (AD) is the most common cause of dementia, accounting for 50% to 60% of cases and affecting nearly 6 million people in the United States. Definitive diagnosis requires either antemortem brain biopsy or postmortem autopsy. However, clinical neuroimaging has been playing a greater role in the diagnosis and management of AD, and several PET tracers approach the sensitivity of tissue diagnosis in identifying AD pathologic condition. This review will focus on the utility of PET imaging in the setting of cognitive impairment, with an emphasis on its role in the diagnosis of AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer disease; Amyloid; Dementia; Neurodegeneration; Positron emission tomography; Tau.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
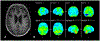
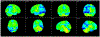
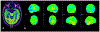
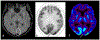
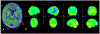
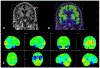
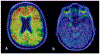
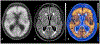
References
-
- Alzheimer’s Association. 2019 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Accessed March 20, 2022. https://www.alz.org/media/documents/alzheimers-facts-and-figures-2019-r.pdf.
-
- Thal DR, Rub U, Orantes M, Braak H. Phases of A beta-deposition in the human brain and its relevance for the development of AD. Neurology 2002;58:1791–1800. - PubMed
-
- Braak H, Braak E. Evolution of the neuropathology of Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl 1996;165:3–12. - PubMed
-
- Kumar ADS. Neuropathology and therapeutic management of Alzheimer’s disease - An update. Drugs Future 2008;33:433.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

