Rapid LC-MS assay for targeted metabolite quantification by serial injection into isocratic gradients
- PMID: 36443449
- PMCID: PMC9823034
- DOI: 10.1007/s00216-022-04384-x
Rapid LC-MS assay for targeted metabolite quantification by serial injection into isocratic gradients
Abstract
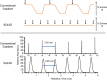
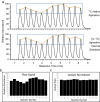
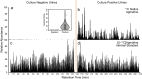
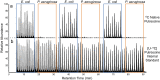
Liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (LC-MS) has emerged as a mainstream strategy for metabolomics analyses. One advantage of LC-MS is that it can serve both as a biomarker discovery tool and as a platform for clinical diagnostics. Consequently, it offers an exciting opportunity to potentially transition research studies into real-world clinical tools. One important distinction between research versus diagnostics-based applications of LC-MS is throughput. Clinical LC-MS must enable quantitative analyses of target molecules in hundreds or thousands of samples each day. Currently, the throughput of these clinical applications is limited by the chromatographic gradient lengths, which-when analyzing complex metabolomics samples-are difficult to conduct in under ~ 3 min per sample without introducing serious quantitative analysis problems. To address this shortcoming, we developed sequential quantification using isotope dilution (SQUID), an analytical strategy that combines serial sample injections into a continuous isocratic mobile phase to maximize throughput. SQUID uses internal isotope-labelled standards to correct for changes in LC-MS response factors over time. We show that SQUID can detect microbial polyamines in human urine specimens (lower limit of quantification; LLOQ = 106 nM) with less than 0.019 normalized root mean square error. Moreover, we show that samples can be analyzed in as little as 57 s. We propose SQUID as a new, high-throughput LC-MS tool for quantifying small sets of target biomarkers across large cohorts.
Keywords: Diagnostics; High-throughput screening; LC–MS; Metabolomics.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
I.A.L., R.A.G., and D.B.G. submitted a patent (WO/2019/227235) describing the use of LC–MS for the detection of urinary tract infections. All other authors have no competing interests. This research was funded by a Genome Canada GAPP award, which is intended to enable the commercialization of research findings.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

