In vivo efficacy of a polymer layered decellularized matrix composite as a cell honing cardiovascular tissue substitute
- PMID: 36444341
- PMCID: PMC9700326
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2022.100451
In vivo efficacy of a polymer layered decellularized matrix composite as a cell honing cardiovascular tissue substitute
Abstract
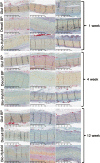
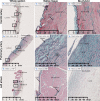
Cardiovascular surgery involves reconstruction of tissues that are under cyclical mechanical loading, and in constant contact with pulsatile blood flow. Durable biomaterials for such tissue reconstruction are scarce, as they need to be mechanically strong, hemocompatible, and resist structural deterioration from calcification. While homografts are ideal, they are scarce; xenografts are immunogenic and rendered inactive from glutaraldehyde fixation, causing them to calficy and structurally deteriorate over time; decellularized xenografts are devoid of cells, mechanically weak; and synthetic polymeric scaffolds are thrombogenic or too dense to enable host cell infiltration. In this work, we report the in vivo feasibility of a new polymer-decellularized matrix composite material (decellularized bovine pericardium-polycaprolactone: chitosan) fabricated by electrospinning, which is designed to be mechanically strong and achieve programmed host cell honing to integrate into the host. In a rodent and sheep model, this new material was found to be hemocompatible, and enabled host cell infiltration into the polymer and the decellularized matrix core underlying the polymer. Presence of M2 macrophages and several vascular cell types, with matrix remodeling in the vicinity of the cells was observed in the explanted tissues. In summary, the proposed composite material is a novel approach to create in-situ host integrating tissue substitutes, with better non-thrombogenicity, reduced infections and endocarditis, and potentially the ability to grow with the patient and remodeling into a native tissue structure.
Keywords: BP, Bovine Pericardium; Biomaterial; Cardiovascular; Ch, Chitosan; ECM, Extracellular matrix; Extracellular matrix; Glut, Glutaraldehyde; Glut-BP, Glut fixed untreated BP; H&E, Hematoxylin and Eosin; Inflammation; LDH, Lactate dehydrogenase; PCL, Polycaprolactone; Remodeling; SEM, Scanning Electron Microscopy; WBC, White blood cell; α-SMA, α smooth muscle actin cells.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Jahnavi Mudigonda reports financial support was provided by American Heart Association. Muralidhar Padala reports financial support was provided by Carlyle Fraser Heart Center at Emory University Hospital Midtown. Muralidhar Padala reports a relationship with Nyra Medical, Inc and Heart Repair Technologies that includes: consulting or advisory and equity or stocks. Muralidhar Padala and Jahnavi Mudigonda has patent #PCT/US21/58 063 pending to PCT.
Figures























References
-
- Karamlou T., Blackstone E.H., Hawkins J.A., Jacobs M.L., Kanter K.R., Brown J.W., Mavroudis C., Caldarone C.A., Williams W.G., McCrindle B.W. Can pulmonary conduit dysfunction and failure be reduced in infants and children less than age 2 years at initial implantation? J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2006;132:829–838. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2006.06.034. e5. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

