Relationship between the Expression of BRAF V600E and Ki-67 with the Recurrence of Well-Differentiated Thyroid Cancer
- PMID: 36444572
- PMCID: PMC9930947
- DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2022.23.11.3617
Relationship between the Expression of BRAF V600E and Ki-67 with the Recurrence of Well-Differentiated Thyroid Cancer
Abstract
Objective: This study aims to determine the relationship between BRAF V600E and Ki-67 expression with the recurrence of well-differentiated thyroid cancers.
Method: The design of this study is a case-control and survival analysis. The data was taken from the thyroid cancer registry in Padang, Indonesia, where samples were taken from well-differentiated thyroid cancer patients who underwent therapy according to the protocol between 2015 and 2020. During this period, 396 well-differentiated thyroid cancer cases were obtained, of which 24 cases experienced recurrence. Of the cases that recurred, we found as many as 20 cases with complete tissue preservation documents later designated as cases. Calculating the expression of BRAF V600E and Ki-67 was performed semi-quantitatively per 100 tumor cells at random. For statistical tests, chi-square and survival analysis were performed using Kaplan-Meier and Cox regression analysis using a computer program with a determined significance level of p < 0.05.
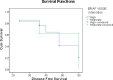
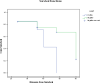
Result: BRAF V600E expression was found in all cases and controls in which 85% of cases had vigorous intensity and 15% had moderate intensity. Ki-67 expression was found positive in 35% of the recurrent cases, while in control, there was no expression of Ki-67. Patients with positive Ki-67 expression had shorter median survival than patients with negative Ki-67 expression of 40 months (95% CI 35-45 months) to 60 months (95% CI 53-67 months). An association was obtained between Ki-67 expression and thyroid cancer recurrence based on disease-free survival (p<0.05) with HR 1.34 (95% CI 1.13-1.92).
Conclusion: This study confirms the association between Ki-67 expression and thyroid cancer recurrence based on disease-free survival and can be used as alternative to support the significance of Ki-67 as a predictor of thyroid cancer recurrence. In addition, Ki-67 can complement other molecular markers such as the BRAF V600E, to increase its prognostic strength.
Keywords: BRAF V600E; Ki-67; Recurrence; Thyroid cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association between BRAF V600E mutation and recurrence of papillary thyroid cancer.J Clin Oncol. 2015 Jan 1;33(1):42-50. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.56.8253. Epub 2014 Oct 20. J Clin Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25332244 Free PMC article.
-
Role and relevance of BRAF mutations in risk stratifying patients of papillary thyroid cancers along with a review of literature.Indian J Cancer. 2017 Jan-Mar;54(1):372-378. doi: 10.4103/ijc.IJC_182_17. Indian J Cancer. 2017. PMID: 29199726
-
The BRAF(V600E) mutation influences the short- and medium-term outcomes of classic papillary thyroid cancer, but is not an independent predictor of unfavorable outcome.Thyroid. 2014 Aug;24(8):1267-74. doi: 10.1089/thy.2013.0675. Epub 2014 Jun 11. Thyroid. 2014. PMID: 24787545
-
Clinical significance of BRAF (V600E) mutation and Ki-67 labeling index in papillary thyroid carcinomas.Anticancer Res. 2007 Sep-Oct;27(5B):3645-9. Anticancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17972530
-
BRAF V600E and TERT promoter mutations cooperatively identify the most aggressive papillary thyroid cancer with highest recurrence.J Clin Oncol. 2014 Sep 1;32(25):2718-26. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.55.5094. Epub 2014 Jul 14. J Clin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25024077 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Possible Markers for Distinguishing benign and Malignant Thyroid Tumors and Predicting Malignancy in Patients with Genetic Predisposition to Cancer.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2024 Feb 1;25(2):465-472. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2024.25.2.465. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2024. PMID: 38415532 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-EGFR/BRAF-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Thyroid Carcinoma.Cancer Diagn Progn. 2023 Mar 3;3(2):151-156. doi: 10.21873/cdp.10194. eCollection 2023 Mar-Apr. Cancer Diagn Progn. 2023. PMID: 36875315 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of stratified management of Ki-67 on the prognosis of small-cell lung cancer.BMC Cancer. 2025 Jul 21;25(1):1197. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-14445-w. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40691591 Free PMC article.
-
Could Oxidative Stress Play a Role in the Development and Clinical Management of Differentiated Thyroid Cancer?Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jun 14;15(12):3182. doi: 10.3390/cancers15123182. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37370792 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical and Paraclinical Considerations Regarding ki67's Role in the Management of Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma-A Literature Review.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 May 7;60(5):769. doi: 10.3390/medicina60050769. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 38792952 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arshad H, Ahmad Z, Hasan SH. Gliomas: correlation of histologic grade, Ki67 and p53 expression with patient survival. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2010;11:1637–40. - PubMed
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Cañadas Garre M, López de la Torre Casares M, Becerra Massare P, et al. BRAF(T1799A) mutation in the primary tumor as a marker of risk, recurrence, or persistence of papillary thyroid carcinoma. Endocrinol Nutr. 2011;58:175–84. - PubMed
-
- Choudhury M, Singh S, Agarwal S. Diagnostic utility of Ki67 and p53 immunostaining on solitary thyroid nodule--a cytohistological and radionuclide scintigraphic study. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2011;54:472–5. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials