A Comparison of the Characteristics of Cytokine Storm between Lichen Planus and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 36444597
- PMCID: PMC9930956
- DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2022.23.11.3843
A Comparison of the Characteristics of Cytokine Storm between Lichen Planus and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
Introduction: Lichen planus (LP) is a relatively common chronic mucocutaneous disease that affects the skin and mucous membranes, including oral mucosa. The etiology of the disease is unknown. Some evidence suggests that the immune system and inflammation may play a role in the formation and progression of lichen planus. Some authorities believe that LP is a precancerous condition. The purpose of this study was to investigate the serum levels of the inflammatory cytokines CRP, IL-1, IL-6, and TNF- in patients with oral lichen planus and oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC), as well as to assess the relationship between these cytokine levels and clinical symptoms.
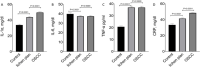
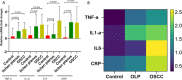
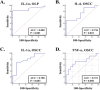
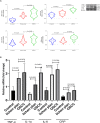
Methods: A total of 75 subjects, with 25 in each group of oral lichen planus, healthy control, and oral squamous cell carcinoma, participated in this cross-sectional study. Serum levels of IL-1α, TNF-α, IL-6, and CRP were determined and compared. In comparison to the healthy control group, the lichen planus and oral squamous cell carcinoma groups had higher levels of CRP, IL-1α, IL-6, and TNF-α.
Results: We discovered that the mean mRNA and protein levels of CRP, IL-1α, IL-6, and TNF-α were significantly higher in the blood and tissue of lichen planus and OSCC patients than in normal controls.
Conclusion: Higher levels of CRP, IL-1α, IL-6, and TNF-α may be linked to OLP and oral carcinogenesis. More research with larger groups is required.
Keywords: CRP; Oral lichen planus; Serum cytokines; TNF-α oral squamous cell carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The feasibility of monitoring NF-kappaB associated cytokines: TNF-alpha, IL-1alpha, IL-6, and IL-8 in whole saliva for the malignant transformation of oral lichen planus.Mol Carcinog. 2005 Oct;44(2):77-82. doi: 10.1002/mc.20113. Mol Carcinog. 2005. PMID: 16075467
-
Expressions of Interleukin-27 in Oral Lichen Planus, Oral Leukoplakia, and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Inflammation. 2022 Jun;45(3):1023-1038. doi: 10.1007/s10753-021-01599-5. Epub 2022 Jan 22. Inflammation. 2022. PMID: 35064378
-
Serum and salivary levels of lactate dehydrogenase in oral squamous cell carcinoma, oral lichen planus and oral lichenoid reaction.BMC Oral Health. 2020 Nov 10;20(1):314. doi: 10.1186/s12903-020-01306-0. BMC Oral Health. 2020. PMID: 33167957 Free PMC article.
-
Updates on immunological mechanistic insights and targeting of the oral lichen planus microenvironment.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 9;13:1023213. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1023213. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36700192 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of Potential Risk Factors that contribute to Malignant Transformation of Oral Lichen Planus: A Literature Review.J Contemp Dent Pract. 2016 Aug 1;17(8):692-701. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1914. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2016. PMID: 27659090 Review.
Cited by
-
Salivary biomarkers: a promising approach for predicting immunotherapy response in head and neck cancers.Clin Transl Oncol. 2025 May;27(5):1887-1920. doi: 10.1007/s12094-024-03742-8. Epub 2024 Oct 8. Clin Transl Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39377974 Review.
-
Analysis of preoperative serum cytokine levels in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 19;15(1):13537. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-89816-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40253468 Free PMC article.
-
Loc646329 sponges miR-21 to reduce RAS/MAP kinase signaling pathway in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC).Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Jun;398(6):6755-6763. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03671-x. Epub 2024 Dec 14. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39673637
-
Evaluation of PPAR-α, PPAR-γ, TLR2, TLR4 Gene Expression In Patients with Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): An Experimental Study.Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2024 Nov 5;38:128. doi: 10.47176/mjiri.38.128. eCollection 2024. Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2024. PMID: 39968463 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Player of Platelet in the Pathogenesis of Cardiotoxicity: Molecular Insight and Future Perspective.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2024 Dec;24(12):1381-1394. doi: 10.1007/s12012-024-09924-8. Epub 2024 Oct 14. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39397196 Review.
References
-
- Allavena P, Garlanda C, Borrello MG, Sica A, Mantovani A. Pathways connecting inflammation and cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2008;18:3–10. - PubMed
-
- Balkwill F, Mantovani A. Inflammation and cancer: back to Virchow? Lancet. 2001;57:539–45. - PubMed
-
- Brailo V, Vucićević-Boras V, Cekić-Arambasin A, et al. The significance of salivary interleukin 6 and tumor necrosis factor alpha in patients with oral leukoplakia. Oral Oncol. 2006;42:370–3. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

