Expanding the clinical spectrum of idiopathic intracranial hypertension
- PMID: 36444979
- PMCID: PMC9835678
- DOI: 10.1097/WCO.0000000000001131
Expanding the clinical spectrum of idiopathic intracranial hypertension
Abstract
Purpose of review: Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH) is a disorder of raised intracranial pressure (ICP). Although the majority of patients with IIH present classically with headache and papilledema, some patients may have unusual presentations or manifestations. Recent advancements in neuroimaging have facilitated the identification of other presentations associated with IIH. This review provides an overview of the expanding clinical spectrum of IIH.
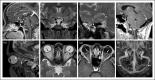
Recent findings: Presentations of IIH that are considered unusual include highly asymmetric or unilateral papilledema, IIH without papilledema, and IIH associated with cranial nerve involvement. These presentations likely reflect differences in the way cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) pressure is transmitted intracranially. Radiological signs of intracranial hypertension are increasingly recognized in patients with IIH and provide further insights into the effects of raised ICP on intracranial structures. Osseous changes in the skull base leading to formation of meningoceles and encephaloceles have been identified in patients with IIH, spontaneous skull base CSF leak, and drug-resistant temporal lobe epilepsy, suggesting a possible association.
Summary: Clinicians should be familiar with the expanding clinical spectrum of IIH and the implications for the management of these presentations.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Mollan SP, Grech O, Sinclair AJ. Headache attributed to idiopathic intracranial hypertension and persistent postidiopathic intracranial hypertension headache: a narrative review. Headache 2021; 61:808–816. - PubMed
-
This review article provides an excellent overview of IIH with a focus on headache, co-existing conditions that may influence headache, and headache management (weight management, medical management and surgical procedures).
-
- Friedman DI, Liu GT, Digre KB. Revised diagnostic criteria for the pseudotumor cerebri syndrome in adults and children. Neurology 2013; 81:1159–1165. - PubMed
-
- Vosoughi AR, Margolin EA, Micieli JA. Idiopathic intracranial hypertension: incidental discovery versus symptomatic presentation. J Neuroophthalmol 2022; 42:187–191. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

