Nutrient deprivation and hypoxia alter T cell immune checkpoint expression: potential impact for immunotherapy
- PMID: 36445478
- PMCID: PMC10349772
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-022-04440-0
Nutrient deprivation and hypoxia alter T cell immune checkpoint expression: potential impact for immunotherapy
Abstract
Aim: Use of immune checkpoint blockade to enhance T cell-mediated immunity within the hostile tumour microenvironment (TME) is an attractive approach in oesophageal adenocarcinoma (OAC). This study explored the effects of the hostile TME, including nutrient deprivation and hypoxia, on immune checkpoint (IC) expression and T cell phenotypes, and the potential use of nivolumab to enhance T cell function under such conditions.
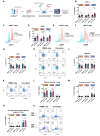
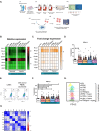
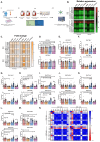
Methods and results: ICs were upregulated on stromal immune cells within the tumour including PD-L2, CTLA-4 and TIGIT. OAC patient-derived PBMCs co-cultured with OE33 OAC cells upregulated LAG-3 and downregulated the co-stimulatory marker CD27 on T cells, highlighting the direct immunosuppressive effects of tumour cells on T cells. Hypoxia and nutrient deprivation altered the secretome of OAC patient-derived PBMCs, which induced upregulation of PD-L1 and PD-L2 on OE33 OAC cells thus enhancing an immune-resistant phenotype. Importantly, culturing OAC patient-derived PBMCs under dual hypoxia and glucose deprivation, reflective of the conditions within the hostile TME, upregulated an array of ICs on the surface of T cells including PD-1, CTLA-4, A2aR, PD-L1 and PD-L2 and decreased expression of IFN-γ by T cells. Addition of nivolumab under these hostile conditions decreased the production of pro-tumorigenic cytokine IL-10.
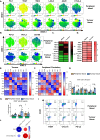
Conclusion: Collectively, these findings highlight the immunosuppressive crosstalk between tumour cells and T cells within the OAC TME. The ability of nivolumab to suppress pro-tumorigenic T cell phenotypes within the hostile TME supports a rationale for the use of immune checkpoint blockade to promote anti-tumour immunity in OAC. Study schematic: (A) IC expression profiles were assessed on CD45+ cells in peripheral whole blood and infiltrating tumour tissue from OAC patients in the treatment-naïve setting. (B) PBMCs were isolated from OAC patients and expanded ex vivo for 5 days using anti-CD3/28 + IL-2 T cell activation protocol and then co-cultured for 48 h with OE33 cells. T cell phenotypes were then assessed by flow cytometry. (C) PBMCs were isolated from OAC patients and expanded ex vivo for 5 days using anti-CD3/28 + IL-2 T cell activation protocol and then further cultured under conditions of nutrient deprivation or hypoxia for 48 h and T cell phenotypes were then assessed by flow cytometry.
Key findings: (A) TIGIT, CTLA-4 and PD-L2 were upregulated on CD45+ immune cells and CTLA-4 expression on CD45+ cells correlated with a subsequent decreased response to neoadjuvant regimen. (B) Following a 48 h co-culture with OE33 cells, T cells upregulated LAG-3 and decreased CD27 co-stimulatory marker. (C) Nutrient deprivation and hypoxia upregulated a range of ICs on T cells and decreased IFN-γ production by T cells. Nivolumab decreased IL-10 production by T cells under nutrient deprivation-hypoxic conditions.
Keywords: Glucose deprivation; Hypoxia; Immune checkpoints; Oesophageal adenocarcinoma; Tumour microenvironment.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Figures

Similar articles
-
HDAC6 inhibition by ITF3756 modulates PD-L1 expression and monocyte phenotype: insights for a promising immune checkpoint blockade co-treatment therapy.Front Immunol. 2025 May 13;16:1546939. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1546939. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40433358 Free PMC article.
-
Oncolytic reovirus enhances the effect of CEA immunotherapy when combined with PD1-PDL1 inhibitor in a colorectal cancer model.Immunotherapy. 2025 Apr;17(6):425-435. doi: 10.1080/1750743X.2025.2501926. Epub 2025 May 12. Immunotherapy. 2025. PMID: 40353308
-
ANV600 is a novel PD-1 targeted IL-2Rβγ agonist that selectively expands tumor antigen-specific T cells and potentiates PD-1 checkpoint inhibitor therapy.J Immunother Cancer. 2025 Jul 15;13(7):e011905. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2025-011905. J Immunother Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40664449 Free PMC article.
-
Nivolumab for adults with Hodgkin's lymphoma (a rapid review using the software RobotReviewer).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jul 12;7(7):CD012556. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012556.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30001476 Free PMC article.
-
New horizons in B-cell lymphoma immunotherapy: From immune checkpoints to precision medicine.Neoplasia. 2025 Sep;67:101206. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2025.101206. Epub 2025 Jul 1. Neoplasia. 2025. PMID: 40592237 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Research Hotspots and Trends in Global Cancer immunometabolism:A Bibliometric Analysis from 2000 to 2023.J Multidiscip Healthc. 2024 Nov 12;17:5117-5137. doi: 10.2147/JMDH.S495330. eCollection 2024. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2024. PMID: 39553266 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neoleukin-2/15-armored CAR-NK cells sustain superior therapeutic efficacy in solid tumors via c-Myc/NRF1 activation.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025 Mar 3;10(1):78. doi: 10.1038/s41392-025-02158-2. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025. PMID: 40025022 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic effect of fully human anti-Nrp-1 antibody on non-small cell lung cancer in vivo and in vitro.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2025 Jan 3;74(2):50. doi: 10.1007/s00262-024-03893-1. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2025. PMID: 39751948 Free PMC article.
-
The future of combination immunotherapy in oesophageal adenocarcinoma.Front Immunol. 2023 Jul 14;14:1217132. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1217132. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37520544 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Effects of virus-induced immunogenic cues on oncolytic virotherapy.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 21;14(1):28861. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-80542-8. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39572761 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ascierto PA et al (2017) Efficacy of BMS-986016, a monoclonal antibody that targets lymphocyte activation gene-3 (LAG-3), in combination with nivolumab in pts with melanoma who progressed during prior anti–PD-1/PD-L1 therapy (mel prior IO) in all-comer and biomarker-enrich. Ann Oncol 28:v611–v612
-
- Camisaschi C et al (2010) LAG-3 expression defines a subset of CD4+CD25highFoxp3+ regulatory T cells that are expanded at tumor sites. J Immunol 184:6545–6551 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

