Learning curve and surgical outcome of robotic assisted colorectal surgery with ERAS program
- PMID: 36446802
- PMCID: PMC9709162
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-24665-w
Learning curve and surgical outcome of robotic assisted colorectal surgery with ERAS program
Abstract
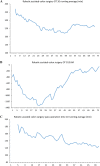
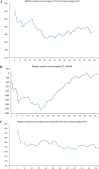
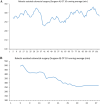
This study analyzed learning curve and the surgical outcome of robotic assisted colorectal surgery with ERAS program. The study results serve as a reference for future robotic colorectal surgeon who applied ERAS in clinical practice. This was a retrospective case-control study to analyze the learning curve of 141 robotic assisted colorectal surgery (RAS) by Da Vinci Xi (Xi) system and compare the surgical outcomes with 147 conventional laparoscopic (LSC) surgery in the same team. Evaluation for maturation was performed by operation time and the CUSUM plot. Patients were recruited from 1st February 2019 to 9th January 2022; follow-up was conducted at 30 days, and the final follow-up was conducted on 9th February 2022. It both took 31 cases for colon and rectal robotic surgeries to reach the maturation phase. Teamwork maturation was achieved after 60 cases. In the maturation stage, RAS required a longer operation time (mean: colon: 249.5 ± 46.5 vs. 190.3 ± 57.3 p < 0.001; rectum 314.9 ± 59.6 vs. 223.6 ± 63.5 p < 0.001). After propensity score matching, robotic surgery with ERAS program resulted in significant shorter length of hospital stay (mean: colon: 5.5 ± 4.5 vs. 10.0 ± 11.9, p < 0.001; rectum: 5.4 ± 3.5 vs. 10.1 ± 7.0, p < 0.001), lower minor complication rate (colon: 6.0% vs 20.0%, p = 0.074 ; rectum: 11.1% vs 33.3%, p = 0.102), and no significant different major complication rate (colon: 2.0% vs 6.0%, p = 0.617; rectum: 7.4% cs 7.4%, p = 1.0) to conventional LSC. Learning curve for robotic assisted colorectal surgery takes 31 cases. Robotic surgery with ERAS program brings significant faster recovery and fewer complication rate compared to laparoscopy in colorectal surgery.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prior experience in laparoscopic rectal surgery can minimise the learning curve for robotic rectal resections: a cumulative sum analysis.Surg Endosc. 2017 Oct;31(10):4067-4076. doi: 10.1007/s00464-017-5453-9. Epub 2017 Mar 7. Surg Endosc. 2017. PMID: 28271267
-
The Learning Curve of Robotic-Assisted Low Rectal Resection of a Novice Rectal Surgeon.World J Surg. 2016 Feb;40(2):456-62. doi: 10.1007/s00268-015-3251-x. World J Surg. 2016. PMID: 26423674
-
Developing a robotic colorectal cancer surgery program: understanding institutional and individual learning curves.Surg Endosc. 2017 Jul;31(7):2820-2828. doi: 10.1007/s00464-016-5292-0. Epub 2016 Nov 4. Surg Endosc. 2017. PMID: 27815742 Free PMC article.
-
Laparoscopic and robotic sacropexy: retrospective review of learning curve experiences and follow-up.Ceska Gynekol. 2017 Fall;82(4):261-267. Ceska Gynekol. 2017. PMID: 28925269 Review. English.
-
Appraisal and Current Considerations of Robotics in Colon and Rectal Surgery.J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2019 Feb;29(2):152-158. doi: 10.1089/lap.2018.0571. Epub 2018 Oct 16. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2019. PMID: 30325690 Review.
Cited by
-
Robotic Plastic Surgery Education: Developing a Robotic Surgery Training Program Specific to Plastic Surgery Trainees.Semin Plast Surg. 2023 Aug 4;37(3):157-167. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-1771026. eCollection 2023 Aug. Semin Plast Surg. 2023. PMID: 38444955 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of DaVinci simulator competitions on medical student interest in robotic surgery.J Robot Surg. 2025 Mar 3;19(1):94. doi: 10.1007/s11701-025-02240-5. J Robot Surg. 2025. PMID: 40029509
-
A Review of the Current Trends and Future Perspectives of Robots in Colorectal Surgery: What Have We Got Ourselves Into?Cureus. 2025 Jan 20;17(1):e77690. doi: 10.7759/cureus.77690. eCollection 2025 Jan. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 39974228 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessing the learning curve in robot-assisted intracorporeal colorectal anastomosis and transrectal extraction (NICE) procedure: from Initial Learning to Mastery.J Robot Surg. 2025 Jun 17;19(1):300. doi: 10.1007/s11701-025-02467-2. J Robot Surg. 2025. PMID: 40526277
-
Robotic-Assisted Colon Cancer Surgery: Faster Recovery and Less Pain Compared to Laparoscopy in a Retrospective Propensity-Matched Study.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jan 13;17(2):243. doi: 10.3390/cancers17020243. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39858025 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

