Graft and Patient Survival Rate among Iranian Pediatric Recipients of Kidney Transplantation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 36447982
- PMCID: PMC9659540
- DOI: 10.18502/ijph.v51i6.9666
Graft and Patient Survival Rate among Iranian Pediatric Recipients of Kidney Transplantation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: The End Stage Renal Disease (ESRD) is irreversible impairment of renal function, to the extent that the patient becomes permanently dependent on alternative therapies, especially in children. We aimed to evaluate the graft and patient survival rate among iranian pediatric recipients of kidney transplantation through a systematic review and meta-analysis.
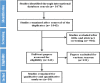
Methods: National (SID, MagIran, IranMedex, IranDoc) and international (Cochrane, Embase, ScienceDirect, Scopus, PubMed, and Web of Science) databases of, were searched to find studies published electronically from 1985 until Nov 2019. Heterogeneity between the collected studies was determined using the Cochran's test (Q) and I2. Meta-regression was used to investigate the factors affecting statistical heterogeneity in 1, 5, and 10-year survival of kidney transplantation in addition to subgroup analysis based on cities.
Results: Ten studies were qualified to enter the meta-analysis. The total participants in the study were 2673 people with an average age of 13.71±3.65 years. In the random-effects model, the survival rate of 1, 3, 5 and 10 yr of kidney transplantation were 91, 88, 81 and 70%, respectively.
Conclusion: By providing the documented and comprehensive evidence, can be the basis of many plans, policies, and decisions of various sectors of development. These sectors include the evaluation of treatment programs and health interventions in the pediatric kidney transplantation. The results of the present study can provide an acceptable estimate of the survival rate of transplanted children in Iran and will be useful for planning prevention and treatment programs.
Keywords: End stage renal disease; Graft survival; Kidney transplantation; Meta-analysis; Patient survival.
Copyright © 2022 Shajari et al. Published by Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Graft and Patient Survival Rates in Kidney Transplantation, and Their Associated Factors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Iran J Public Health. 2021 Aug;50(8):1555-1563. doi: 10.18502/ijph.v50i8.6801. Iran J Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34917526 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effect of exercise on anxiety in the elderly worldwide: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2020 Nov 11;18(1):363. doi: 10.1186/s12955-020-01609-4. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2020. PMID: 33176811 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of Hypertension in Renal Diseases in Iran: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Int J Prev Med. 2019 Jul 5;10:124. doi: 10.4103/ijpvm.IJPVM_522_18. eCollection 2019. Int J Prev Med. 2019. PMID: 31367287 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The incidence of prostate cancer in Iran: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Prostate Int. 2018 Jun;6(2):41-45. doi: 10.1016/j.prnil.2017.11.003. Epub 2017 Dec 8. Prostate Int. 2018. PMID: 29922630 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of physical exercise on the fatigue symptoms in patients with multiple sclerosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Neurol. 2020 Mar 13;20(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s12883-020-01654-y. BMC Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32169035 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Knowledge, attitude, and practice toward postoperative self-management among kidney transplant recipients.BMC Med Educ. 2024 Jun 11;24(1):652. doi: 10.1186/s12909-024-05631-8. BMC Med Educ. 2024. PMID: 38862944 Free PMC article.
-
A retrospective analysis of prenatal genetic results in fetal hydronephrosis.PLoS One. 2025 May 22;20(5):e0324734. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0324734. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40403082 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ghelichi Ghojogh M, Taghizadeh Afshari A, Salarilak S, et al. (2017). The Effect of Body Mass Index on Patient and Graft Survival Rate in Kidney Transplanted Patients in Iran. Nephro-Urol Mon, 9(4): e14386.
-
- Einollahi B, Pourfarziani V, Ahmadzad-Asl M, et al. (2007). Iranian model of renal allograft transplantation in 3028 recipients: survival and risk factors. Transplant Proc, 39(4):907–10. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
