Emerging 0D, 1D, 2D, and 3D nanostructures for efficient point-of-care biosensing
- PMID: 36448023
- PMCID: PMC9691282
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biosx.2022.100284
Emerging 0D, 1D, 2D, and 3D nanostructures for efficient point-of-care biosensing
Abstract
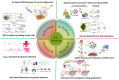
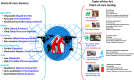
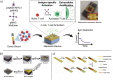
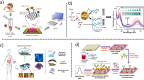
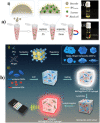
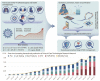
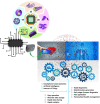
The recent COVID-19 infection outbreak has raised the demand for rapid, highly sensitive POC biosensing technology for intelligent health and wellness. In this direction, efforts are being made to explore high-performance nano-systems for developing novel sensing technologies capable of functioning at point-of-care (POC) applications for quick diagnosis, data acquisition, and disease management. A combination of nanostructures [i.e., 0D (nanoparticles & quantum dots), 1D (nanorods, nanofibers, nanopillars, & nanowires), 2D (nanosheets, nanoplates, nanopores) & 3D nanomaterials (nanocomposites and complex hierarchical structures)], biosensing prototype, and micro-electronics makes biosensing suitable for early diagnosis, detection & prevention of life-threatening diseases. However, a knowledge gap associated with the potential of 0D, 1D, 2D, and 3D nanostructures for the design and development of efficient POC sensing is yet to be explored carefully and critically. With this focus, this review highlights the latest engineered 0D, 1D, 2D, and 3D nanomaterials for developing next-generation miniaturized, portable POC biosensors development to achieve high sensitivity with potential integration with the internet of medical things (IoMT, for miniaturization and data collection, security, and sharing), artificial intelligence (AI, for desired analytics), etc. for better diagnosis and disease management at the personalized level.
Keywords: 0D to 3D nanomaterials; Biosensors; Efficient diagnostics; Personalized health management; Point-of-care testing; Wearable.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
From Nanosystems to a Biosensing Prototype for an Efficient Diagnostic: A Special Issue in Honor of Professor Bansi D. Malhotra.Biosensors (Basel). 2021 Sep 29;11(10):359. doi: 10.3390/bios11100359. Biosensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34677315 Free PMC article.
-
Electrochemical SARS-CoV-2 Sensing at Point-of-Care and Artificial Intelligence for Intelligent COVID-19 Management.ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2020 Nov 16;3(11):7306-7325. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.0c01004. Epub 2020 Oct 27. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2020. PMID: 35019473 Review.
-
Internet of medical things (IoMT)-integrated biosensors for point-of-care testing of infectious diseases.Biosens Bioelectron. 2021 May 1;179:113074. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2021.113074. Epub 2021 Feb 6. Biosens Bioelectron. 2021. PMID: 33596516 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanomaterials in point-of-care diagnostics: Bridging the gap between laboratory and clinical practice.Pathol Res Pract. 2024 Nov;263:155685. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2024.155685. Epub 2024 Oct 28. Pathol Res Pract. 2024. PMID: 39471524 Review.
-
Unlocking new frontiers in healthcare: The impact of nano-optical biosensors on personalized medical diagnostics.J Biotechnol. 2025 Apr;400:29-47. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2025.02.005. Epub 2025 Feb 15. J Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 39961549 Review.
Cited by
-
Insights into Structural, Electronic, and Transport Properties of Pentagonal PdSe2 Nanotubes Using First-Principles Calculations.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023 May 25;13(11):1728. doi: 10.3390/nano13111728. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37299633 Free PMC article.
-
Aptamer Based on Silver Nanoparticle-Modified Flexible Carbon Ink Printed Electrode for the Electrochemical Detection of Chikungunya Virus.Biosensors (Basel). 2024 Jul 16;14(7):344. doi: 10.3390/bios14070344. Biosensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39056620 Free PMC article.
-
High-Rate One-Dimensional α-MnO2 Anode for Lithium-Ion Batteries: Impact of Polymorphic and Crystallographic Features on Lithium Storage.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023 Oct 23;13(20):2808. doi: 10.3390/nano13202808. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37887958 Free PMC article.
-
Nanomaterial-Based Biosensors for the Detection of COVID-19.Indian J Microbiol. 2025 Mar;65(1):120-136. doi: 10.1007/s12088-024-01336-0. Epub 2024 Jun 23. Indian J Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40371045
-
An Integrated Approach to Improve the Assay Performance of Quantum Dot-Based Lateral Flow Immunoassays by Using Silver Deposition.Microchem J. 2023 Sep;192:108932. doi: 10.1016/j.microc.2023.108932. Epub 2023 Jun 7. Microchem J. 2023. PMID: 38344211 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Afsahi S., Lerner M.B., Goldstein J.M., Lee J., Tang X., Bagarozzi D.A., Pan D., Locascio L., Walker A., Barron F., Goldsmith B.R. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018;100:85–88. - PubMed
-
- Aghili Z., Nasirizadeh N., Divsalar A., Shoeibi S., Yaghmaei P. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017;95:72–80. - PubMed
-
- Ahmadi A., Khoshfetrat S.M., Kabiri S., Fotouhi L., Dorraji P.S., Omidfar K. IEEE Sensor. 2021;21:9210–9217.
-
- al Lawati H.A.J., Hassanzadeh J. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2020;1139:15–26. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
