Durability of humoral and cell-mediated immune response after SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine administration
- PMID: 36448089
- PMCID: PMC9878094
- DOI: 10.1002/jmv.28360
Durability of humoral and cell-mediated immune response after SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine administration
Abstract
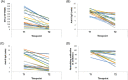
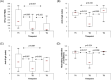
Vaccination against the SARS-Cov-2 virus is an effective way to protect against the disease and the severe course of COVID-19. Forty-nine fully vaccinated with mRNA vaccines (BNT162b2 or mRNA-1273) SARS-CoV-2 infection-naïve volunteers aged 33-89 were enrolled in the study. Evaluation of the cellular and humoral immune response was performed within 1 to 3 months (T1) and 6-9 months (T2) after the second injection, and within 2-3 months (T3) after a booster dose. Additionally, a comparative analysis of the specific immune status was made between two age groups-below 60 (n = 22) and over 60 (n = 27) years. SARS-CoV-2-specific T-cell response was evaluated by IFN-γ-producing spot forming cells (SFCs) using a standardized ELISPOT assay. Virus neutralizing antibodies (VNA) against SARS-CoV-2 were measured by a blocking ELISA test and spike protein specific IgG (S-IgG) and IgA (S-IgA) antibodies-by semiquantitative ELISA. IFN-γ-producing SFCs, S-IgG, S-IgA and VNA significantly decreased 6-9 months after the second dose. After the third injection S-IgG and S-IgA markedly increased compared to T2 and reached the levels at T1. Of note, the highest values of VNA were observed at T3. No differences in the tested immune parameters were found between the two age groups. Data obtained showed that for a long period-6-9 months after a full course of immunization with mRNA vaccine, immune reactivity is present, but both cellular and humoral immune responses gradually decrease. The administration of a third dose mainly restores the specific humoral immune response against the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
Keywords: booster dose; humoral and cell-mediated immune response; mRNA SARS CoV-2 vaccines.
© 2022 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Kinetics and Persistence of the Cellular and Humoral Immune Responses to BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccine in SARS-CoV-2-Naive and -Experienced Subjects: Impact of Booster Dose and Breakthrough Infections.Front Immunol. 2022 May 31;13:863554. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.863554. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35711445 Free PMC article.
-
Humoral immune response after different SARS-CoV-2 vaccination regimens.BMC Med. 2022 Jan 21;20(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s12916-021-02231-x. BMC Med. 2022. PMID: 35057798 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of High Levels of Specific Humoral and Cellular Responses to SARS-CoV-2 After the Administration of Covid-19 mRNA Vaccines Requires Several Days.Front Immunol. 2021 Oct 4;12:726960. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.726960. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34671348 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of the induction of humoral and cellular immunity by third vaccination for SARS-CoV-2.J Infect Chemother. 2024 Oct;30(10):1021-1027. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2024.03.021. Epub 2024 Apr 1. J Infect Chemother. 2024. PMID: 38570139
-
Characterization of SARS-CoV-2-Specific Humoral and Cellular Immune Responses Induced by Inactivated COVID-19 Vaccines in a Real-World Setting.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 22;12:802858. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.802858. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 35003131 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Feline Infectious Peritonitis mRNA Vaccine Elicits Both Humoral and Cellular Immune Responses in Mice.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Jun 24;12(7):705. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12070705. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39066343 Free PMC article.
-
Durability of immune response after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in patients with chronic liver disease.Front Immunol. 2023 Jun 15;14:1200198. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1200198. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37398662 Free PMC article.
-
Prolonged SARS-CoV-2 T Cell Responses in a Vaccinated COVID-19-Naive Population.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Mar 4;12(3):270. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12030270. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38543904 Free PMC article.
-
An mRNA-Based Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccine Elicits Strong Neutralizing Antibody Responses and Protects Rodents Without Vaccine-Associated Enhanced Respiratory Disease.Vaccines (Basel). 2025 Jan 9;13(1):52. doi: 10.3390/vaccines13010052. Vaccines (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39852831 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular Immunity of SARS-CoV-2 in the Borriana COVID-19 Cohort: A Nested Case-Control Study.Epidemiologia (Basel). 2024 Apr 10;5(2):167-186. doi: 10.3390/epidemiologia5020012. Epidemiologia (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38651389 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Food and Drug Administration . Pfizer‐BioNTech COVID‐19 vaccines. https://www.fda.gov/emergency-preparedness-and-response/coronavirus-dise...
-
- European Medicines Agency . EMA recommends first COVID‐19 vaccine for authorisation in the EU. 2020. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/news/ema-recommends-first-covid-19-vaccine-...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

