TXNIP Suppresses the Osteochondrogenic Switch of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells in Atherosclerosis
- PMID: 36448450
- PMCID: PMC9829043
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.122.321538
TXNIP Suppresses the Osteochondrogenic Switch of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells in Atherosclerosis
Abstract
Background: The osteochondrogenic switch of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) is a pivotal cellular process in atherosclerotic calcification. However, the exact molecular mechanism of the osteochondrogenic transition of VSMCs remains to be elucidated. Here, we explore the regulatory role of TXNIP (thioredoxin-interacting protein) in the phenotypical transitioning of VSMCs toward osteochondrogenic cells responsible for atherosclerotic calcification.
Methods: The atherosclerotic phenotypes of Txnip-/- mice were analyzed in combination with single-cell RNA-sequencing. The atherosclerotic phenotypes of Tagln-Cre; Txnipflox/flox mice (smooth muscle cell-specific Txnip ablation model), and the mice transplanted with the bone marrow of Txnip-/- mice were analyzed. Public single-cell RNA-sequencing dataset (GSE159677) was reanalyzed to define the gene expression of TXNIP in human calcified atherosclerotic plaques. The effect of TXNIP suppression on the osteochondrogenic phenotypic changes in primary aortic VSMCs was analyzed.
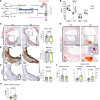
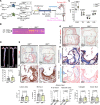
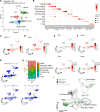
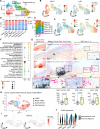
Results: Atherosclerotic lesions of Txnip-/- mice presented significantly increased calcification and deposition of collagen content. Subsequent single-cell RNA-sequencing analysis identified the modulated VSMC and osteochondrogenic clusters, which were VSMC-derived populations. The osteochondrogenic cluster was markedly expanded in Txnip-/- mice. The pathway analysis of the VSMC-derived cells revealed enrichment of bone- and cartilage-formation-related pathways and bone morphogenetic protein signaling in Txnip-/- mice. Reanalyzing public single-cell RNA-sequencing dataset revealed that TXNIP was downregulated in the modulated VSMC and osteochondrogenic clusters of human calcified atherosclerotic lesions. Tagln-Cre; Txnipflox/flox mice recapitulated the calcification and collagen-rich atherosclerotic phenotypes of Txnip-/- mice, whereas the hematopoietic deficiency of TXNIP did not affect the lesion phenotype. Suppression of TXNIP in cultured VSMCs accelerates osteodifferentiation and upregulates bone morphogenetic protein signaling. Treatment with the bone morphogenetic protein signaling inhibitor K02288 abrogated the effect of TXNIP suppression on osteodifferentiation.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that TXNIP is a novel regulator of atherosclerotic calcification by suppressing bone morphogenetic protein signaling to inhibit the transition of VSMCs toward an osteochondrogenic phenotype.
Keywords: TXNIP; atherosclerosis; calcification; osteochondrogenic; vascular smooth muscle cell.
Figures




References
-
- Bentzon JF, Otsuka F, Virmani R, Falk E. Mechanisms of plaque formation and rupture. Circ Res. 2014;114:1852–1866. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.114.302721 - PubMed
-
- Libby P. The changing landscape of atherosclerosis. Nature. 2021;592:524–533. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03392-8 - PubMed
-
- Alexopoulos N, Raggi P. Calcification in atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2009;6:681–688. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2009.165 - PubMed
-
- Greenland P, Bonow RO, Brundage BH, Budoff MJ, Eisenberg MJ, Grundy SM, Lauer MS, Post WS, Raggi P, Redberg RF, et al. . ACCF/AHA 2007 clinical expert consensus document on coronary artery calcium scoring by computed tomography in global cardiovascular risk assessment and in evaluation of patients with chest pain: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation Clinical Expert Consensus Task Force (ACCF/AHA writing committee to update the 2000 Expert consensus document on electron beam computed tomography) developed in collaboration with the society of atherosclerosis imaging and prevention and the society of cardiovascular computed tomography. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007;49:378–402. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2006.10.001 - PubMed
-
- Virmani R, Kolodgie FD, Burke AP, Farb A, Schwartz SM. Lessons from sudden coronary death: a comprehensive morphological classification scheme for atherosclerotic lesions. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2000;20:1262–1275. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.20.5.1262 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

