Phosphofructokinase P fine-tunes T regulatory cell metabolism, function, and stability in systemic autoimmunity
- PMID: 36449620
- PMCID: PMC9710877
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adc9657
Phosphofructokinase P fine-tunes T regulatory cell metabolism, function, and stability in systemic autoimmunity
Abstract
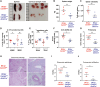
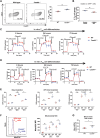
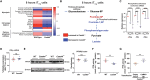
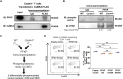
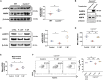
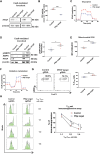
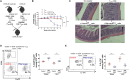
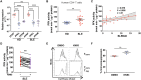
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease characterized by defective regulatory T (Treg) cells. Here, we demonstrate that a T cell-specific deletion of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase 4 (CaMK4) improves disease in B6.lpr lupus-prone mice and expands Treg cells. Mechanistically, CaMK4 phosphorylates the glycolysis rate-limiting enzyme 6-phosphofructokinase, platelet type (PFKP) and promotes aerobic glycolysis, while its end product fructose-1,6-biphosphate suppresses oxidative metabolism. In Treg cells, a CRISPR-Cas9-enabled Pfkp deletion recapitulated the metabolism of Camk4-/- Treg cells and improved their function and stability in vitro and in vivo. In SLE CD4+ T cells, PFKP enzymatic activity correlated with SLE disease activity and pharmacologic inhibition of CaMK4-normalized PFKP activity, leading to enhanced Treg cell function. In conclusion, we provide molecular insights in the defective metabolism and function of Treg cells in SLE and identify PFKP as a target to fine-tune Treg cell metabolism and thereby restore their function.
Figures
References
-
- Tsokos G. C., Systemic lupus erythematosus. N. Engl. J. Med. 365, 2110–2121 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Scherlinger M., Mertz P., Sagez F., Meyer A., Felten R., Chatelus E., Javier R.-M., Sordet C., Martin T., Korganow A.-S., Guffroy A., Poindron V., Richez C., Truchetet M.-E., Blanco P., Schaeverbeke T., Sibilia J., Devillers H., Arnaud L., Worldwide trends in all-cause mortality of auto-immune systemic diseases between 2001 and 2014. Autoimmun. Rev. 19, 102531 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Lee Y. H., Choi S. J., Ji J. D., Song G. G., Overall and cause-specific mortality in systemic lupus erythematosus: An updated meta-analysis. Lupus 25, 727–734 (2016). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

