Did Balanced Crystalloids Really Decrease Mortality in Patients with Sepsis?
- PMID: 36450133
- PMCID: PMC10870897
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.202211-2091LE
Did Balanced Crystalloids Really Decrease Mortality in Patients with Sepsis?
Figures
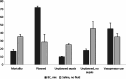
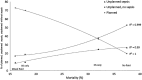
Comment in
-
Reply to Gueret: Did Balanced Crystalloids Really Decrease Mortality in Patients with Sepsis?Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2023 Mar 1;207(5):628-629. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202211-2127LE. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2023. PMID: 36450136 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Comment on
-
Association between Type of Fluid Received Prior to Enrollment, Type of Admission, and Effect of Balanced Crystalloid in Critically Ill Adults: A Secondary Exploratory Analysis of the BaSICS Clinical Trial.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2022 Jun 15;205(12):1419-1428. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202111-2484OC. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2022. PMID: 35349397 Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Zampieri FG, Machado FR, Biondi RS, Freitas FGR, Veiga VC, Figueiredo RC, et al. Association between type of fluid received prior to enrollment, type of admission, and effect of balanced crystalloid in critically ill adults: a secondary exploratory analysis of the BaSICS clinical trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med . 2022;205:1419–1428. - PubMed
-
- Zampieri FG, Machado FR, Biondi RS, Freitas FGR, Veiga VC, Figueiredo RC, et al. BaSICS investigators and the BRICNet members Effect of intravenous fluid treatment with a balanced solution vs 0.9% saline solution on mortality in critically ill patients: the BaSICS randomized clinical trial. JAMA . 2021;326:818–829. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

