Comprehensive transcriptomic profiling and mutational landscape of primary gastric linitis plastica
- PMID: 36450891
- PMCID: PMC9950178
- DOI: 10.1007/s10120-022-01353-2
Comprehensive transcriptomic profiling and mutational landscape of primary gastric linitis plastica
Erratum in
-
Correction: Comprehensive transcriptomic profiling and mutational landscape of primary gastric linitis plastica.Gastric Cancer. 2023 May;26(3):478. doi: 10.1007/s10120-023-01383-4. Gastric Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37017793 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Primary gastric linitis plastica (GLP) is a distinct phenotype of gastric cancer with poor survival. Comprehensive molecular profiles and putative therapeutic targets of GLP remain undetermined.
Methods: We subjected 10 tumor-normal tissue pairs to whole exome sequencing (WES) and whole transcriptome sequencing (WTS). 10 tumor samples were all GLP which involves 100% of the gastric wall macroscopically. TCGA data were compared to generate the top mutated genes and the overexpressed genes in GLP.
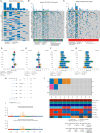
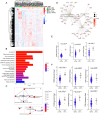
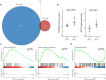
Results: Our results reveal that GLP has distinctive genomic and transcriptomic features, dysfunction in the Hippo pathway is likely to be a key step during GLP development. 6 genes were identified as significantly highly mutated genes in GLP, including AOX1, ANKRD36C, CPXM1, PTPN14, RPAP1, and DCDC1). MUC6, as a previously identified gastric cancer driver gene, has a high mutation rate (20%) in GLP. 20% of patients in our GLP cohort had CDH1 mutations, while none had RHOA mutations. GLP exhibits high immunodeficiency and low AMPK pathway activity. Our WTS results showed that 3 PI3K-AKT pathway-related genes (PIK3R2, AKT3, and IGF1) were significantly up-regulated in GLP. Two genes were identified using immunohistochemistry (IHC), IGF2BP3 and MUC16, which specifically expressed in diffuse-type-related gastric cancer cell lines, and its knockdown inhibits PI3K-AKT pathway activity.
Conclusions: We provide the first integrative genomic and transcriptomic profiles of GLP, which may facilitate its diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment.
Keywords: Gastric cancer (GC); Gastric linitis plastica (GLP); Scirrhous gastric cancer (SGC); Whole exome sequencing (WES); Whole transcriptome sequencing (WTS).
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The Genomic Signatures of Linitis Plastica Signal the Entrance into a New Era: Novel Approaches for Diagnosis and Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 28;24(19):14680. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914680. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The significance of a nineteenth century definition in the era of genomics: linitis plastica.World J Surg Oncol. 2017 Jul 5;15(1):123. doi: 10.1186/s12957-017-1187-3. World J Surg Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28679451 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[An autopsy case of gastric metastasis simulating linitis plastica carcinoma from primary linitis plastica carcinoma of the rectum].Gan No Rinsho. 1988 Nov;34(14):1996-2001. Gan No Rinsho. 1988. PMID: 2849687 Review. Japanese.
-
Endoscopic ultrasound guided fine needle biopsy in patients with suspected gastric linitis plastica.Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2022 May;46(5):101903. doi: 10.1016/j.clinre.2022.101903. Epub 2022 Mar 14. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 35301155
-
Relatively small size linitis plastica of the stomach: multislice CT detection of tissue fibrosis.Abdom Imaging. 2007 Nov;32(6):694-7. doi: 10.1007/s00261-006-9171-3. Epub 2006 Dec 7. Abdom Imaging. 2007. PMID: 17151892
Cited by
-
The Genomic Signatures of Linitis Plastica Signal the Entrance into a New Era: Novel Approaches for Diagnosis and Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 28;24(19):14680. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914680. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic strategies and prognostic challenges in linitis plastica.World J Exp Med. 2025 Mar 20;15(1):96318. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v15.i1.96318. eCollection 2025 Mar 20. World J Exp Med. 2025. PMID: 40115754 Free PMC article.
-
Landscape Analysis of CLDN18 Expression and Isoform Distribution in Solid Tumors: Insights From MONSTAR-SCREEN-2 Study.Cancer Sci. 2025 Aug;116(8):2218-2231. doi: 10.1111/cas.70100. Epub 2025 Jun 2. Cancer Sci. 2025. PMID: 40455642 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive histopathological analysis of gastric cancer in European and Latin America populations reveals differences in PDL1, HER2, p53 and MUC6 expression.Gastric Cancer. 2025 Mar;28(2):160-173. doi: 10.1007/s10120-024-01578-3. Epub 2025 Jan 5. Gastric Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39755998 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting IGF2BP3 in Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 29;24(11):9423. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119423. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37298373 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Leocata P, Ventura L, Giunta M, Guadagni S, Fortunato C, Discepoli S, et al. Gastric carcinoma: a histopathological study of 705 cases. Ann Ital Chir. 1998;69:331–337. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 81972908/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 32271238/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- WKJ-ZJ-2117/National Health Commission Science Research Fund-Zhejiang Provincial Health Key Science and Technology Plan Project
- LZ18H160002/Key Projects from Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation
- LQ19H160005/General Project from Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation
- Zhejiang Provincial CPC Committee Talents [2019]-3/Leading Talents in Scientific and Technological Innovation from Zhejiang Provincial Ten Thousand Talents Plan
- Zjhrss2014-150/Zhejiang Province Health Leader Talent (Zjwjw2021-40), and Major Training Personnel from Zhejiang Provincial Program for Training and Development Project for 151 Talents
- 20IRTSTHN026/Program for Innovation Research Team (in Science and Technology) in University of Henan Province
- 2019ZD025/Zhejiang Medical and Health Science and Technology Project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

