PLD3 affects axonal spheroids and network defects in Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 36450991
- PMCID: PMC9729106
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-05491-6
PLD3 affects axonal spheroids and network defects in Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
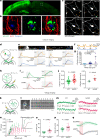
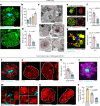
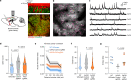
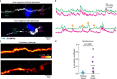
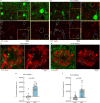
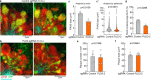
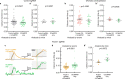
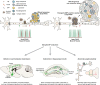
The precise mechanisms that lead to cognitive decline in Alzheimer's disease are unknown. Here we identify amyloid-plaque-associated axonal spheroids as prominent contributors to neural network dysfunction. Using intravital calcium and voltage imaging, we show that a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease demonstrates severe disruption in long-range axonal connectivity. This disruption is caused by action-potential conduction blockades due to enlarging spheroids acting as electric current sinks in a size-dependent manner. Spheroid growth was associated with an age-dependent accumulation of large endolysosomal vesicles and was mechanistically linked with Pld3-a potential Alzheimer's-disease-associated risk gene1 that encodes a lysosomal protein2,3 that is highly enriched in axonal spheroids. Neuronal overexpression of Pld3 led to endolysosomal vesicle accumulation and spheroid enlargement, which worsened axonal conduction blockades. By contrast, Pld3 deletion reduced endolysosomal vesicle and spheroid size, leading to improved electrical conduction and neural network function. Thus, targeted modulation of endolysosomal biogenesis in neurons could potentially reverse axonal spheroid-induced neural circuit abnormalities in Alzheimer's disease, independent of amyloid removal.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
J.G. is a member of the scientific advisory board at Vigil Neuro. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





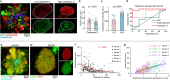
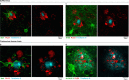
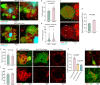
Comment in
-
Swollen axons impair neuronal circuits in Alzheimer's disease.Nature. 2022 Dec;612(7939):218-220. doi: 10.1038/d41586-022-03800-7. Nature. 2022. PMID: 36450951 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 AG066444/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R25 NS079193/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS115544/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 22ZR1415000/National Science Foundation
- P01 AG026276/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG019610/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 NS072026/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG058257/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR019895/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DC009977/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005136/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG003991/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS111961/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066509/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T15 LM007056/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- RR029676-01/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

