Effect of exercise on rehabilitation of breast cancer surgery patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 36451034
- PMCID: PMC10006647
- DOI: 10.1002/nop2.1518
Effect of exercise on rehabilitation of breast cancer surgery patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Aim: To determine the effective exercise methods for different complications of breast cancer patients after surgery.
Design: Systematic review and meta-analysis.
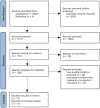
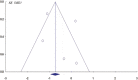
Methods: A comprehensive electronic search was carried out with no time limit until May 2020. Studies must have been randomized controlled trials of patients after breast cancer surgery, without limit to the way of exercise. Literature quality was evaluated by the modified Jadad scale. The meta-analysis was conducted with CMA2.0 software.
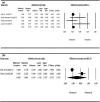
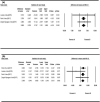
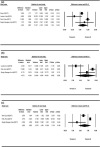
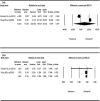
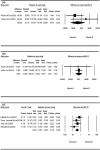
Results: Aerobic exercise reduced the intensity of the pain (MD = -1.043), improved shoulder flexion (MD = 3.398) and internal rotation range (MD = 3.868), lessened upper limb dysfunction (MD = -5.231) and improved muscle strength during flexion (MD = 1.076) and abduction (MD = 0.991). Shoulder elbow movement improved the range of shoulder external rotation (MD = 2.691) and reduced the incidence of arm lymphedema (RR = 0.343). Anti-resistance exercise also lessened upper limb dysfunction (MD = - 4.094).
Keywords: breast cancer; meta-analysis; rehabilitation exercise; surgery.
© 2022 The Authors. Nursing Open published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Ammitzbøll, G. , Andersen, K. G. , Bidstrup, P. E. , Johansen, C. , Lanng, C. , Kroman, N. , Zerahn, B. , Hyldegaard, O. , Andersen, E. W. , & Dalton, S. O. (2020). Effect of progressive resistance training on persistent pain after axillary dissection in breast cancer: A randomized controlled trial. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment, 179, 173–183. 10.1007/s10549-019-05461-z - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bhat, V. , Pellizzari, S. , Allan, A. L. , Wong, E. , Lock, M. , Brackstone, M. , Lohmann, A. E. , Cescon, D. W. , & Parsyan, A. (2022). Radiotherapy and radiosensitization in breast cancer: Molecular targets and clinical applications. Critical reviews in Oncology/Hematology., 169, 103566. 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2021.103566 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Campbell, K. L. , Winters‐Stone, K. M. , Wiskemann, J. , May, A. M. , Schwartz, A. L. , Courneya, K. S. , Zucker, D. S. , Matthews, C. E. , Ligibel, J. A. , Gerber, L. H. , Morris, G. S. , Patel, A. V. , Hue, T. F. , Perna, F. M. , Schmitz, K. M. (2019). Exercise guidelines for cancer survivors: Consensus Statement from international multidisciplinary roundtable. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, 51(11), 2375–2390. 10.1249/MSS.0000000000002116 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

