DEM-TACE as the initial treatment could improve the clinical efficacy of the hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus: a retrospective controlled study
- PMID: 36451104
- PMCID: PMC9714197
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-022-10361-5
DEM-TACE as the initial treatment could improve the clinical efficacy of the hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus: a retrospective controlled study
Abstract
Background: Conventional-transarterial chemoembolization (C-TACE) was proven to improve overall survival (OS) in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients with portal vein tumor thrombus (PVTT), drug-eluting microsphere-TACE (DEM-TACE) was supposed to provide more benefit than C-TACE in this respect.
Purpose: To compare the safety and efficacy between DEM-TACE and C-TACE as the initial treatment in HCC patients with PVTT and to identify prognostic factors of OS.
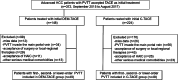
Methods: The medical records of advanced HCC patients with PVTT who underwent DEM-TACE or C-TACE as the initial thearpy from September 2015 with mean follow-up time 14.9 ± 1.2 (95% CI 12.6-17.2) months were retrospectively evaluated. A total of 97 patients were included, 49 patients in the DEM-TACE group and 48 in the C-TACE group. Adverse events (AEs) related to TACE were compared. Tumor and PVTT radiologic response, time to tumor progression (TTP) and OS were calculated and compared in both groups.
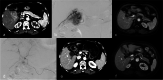
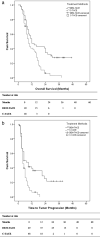
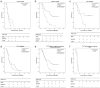
Results: Patients in DEM-TACE group had a better radiologic response (Tumr response: 89.8% vs. 75.0%; PVTT response: 85.7% vs. 70.8%; overall response: 79.6% vs. 58.3%, P = 0.024) and longer TTP (7.0 months vs. 4.0 months, P = 0.040) than patients in C-TACE group. A lower incidence of abdominal pain was found in the DEM-TACE group than in C-TACE group (21 vs. 31, P = 0.032), but there were no significant differences between DEM-TACE and C-TACE patients in any other AEs reported. When compared to C-TACE, DEM-TACE also showed significant OS benefits (12.0 months vs. 9.0 months, P = 0.027). DEM-TACE treatment, the absence of arterioportal shunt (APS), lower AFP value and better PVTT radiologic response were the independent prognostic factors for OS in univariate/multivariate analyses, which provided us with a guide for better patient selection.
Conclusions: Based on our retrospective study, DEM-TACE can be performed safely and might be superior to C-TACE as the initial treatment for HCC patients with PVTT.
Trial registration: Retrospectively registered.
Keywords: Drug-eluting microsphere; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Portal vein tumor thrombosis; Transarterial chemoembolization.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies, whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article.
Figures
References
-
- Global Burden of Disease Liver Cancer Collaboration. Akinyemiju T, Abera S, Ahmed M, Alam N, Alemayohu MA, et al. The burden of primary liver cancer and underlying etiologies from 1990 to 2015 at the global, regional, and national level: results from the global burden of disease study 2015. JAMA Oncol. 2017;3(12):1683–91. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.3055. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

