T1w/FLAIR ratio standardization as a myelin marker in MS patients
- PMID: 36451354
- PMCID: PMC9668645
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nicl.2022.103248
T1w/FLAIR ratio standardization as a myelin marker in MS patients
Abstract
Introduction: Calculation of a T1w/T2w ratio was introduced as a proxy for myelin integrity in the brain of multiple sclerosis (MS) patients. Since nowadays 3D FLAIR is commonly used for lesion detection instead of T2w images, we introduce a T1w/FLAIR ratio as an alternative for the T1w/T2w ratio.
Objectives: Bias and intensity variation are widely present between different scanners, between subjects and within subjects over time in T1w, T2w and FLAIR images. We present a standardized method for calculating a histogram calibrated T1w/FLAIR ratio to reduce bias and intensity variation in MR sequences from different scanners and at different time-points.
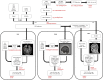
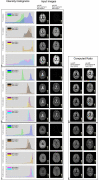
Material and methods: 207 Relapsing Remitting MS patients were scanned on 4 different 3 T scanners with a protocol including 3D T1w, 2D T2w and 3D FLAIR images. After bias correction, T1w/FLAIR ratio maps and T1w/T2w ratio maps were calculated in 4 different ways: without calibration, with linear histogram calibration as described by Ganzetti et al. (2014), and by using 2 methods of non-linear histogram calibration. The first nonlinear calibration uses a template of extra-cerebral tissue and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) brought from Montreal Neurological Institute (MNI) space to subject space; for the second nonlinear method we used an extra-cerebral tissue and CSF template of our own subjects. Additionally, we segmented several brain structures such as Normal Appearing White Matter (NAWM), Normal Appearing Grey Matter (NAGM), corpus callosum, thalami and MS lesions using Freesurfer and Samseg.
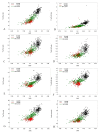
Results: The coefficient of variation of T1w/FLAIR ratio in NAWM for the no calibrated, linear, and 2 nonlinear calibration methods were respectively 24, 19.1, 9.5, 13.8. The nonlinear methods of calibration showed the best results for calculating the T1w/FLAIR ratio with a smaller dispersion of the data and a smaller overlap of T1w/FLAIR ratio in the different segmented brain structures. T1w/T2w and T1w/FLAIR ratios showed a wider range of values compared to MTR values.
Conclusions: Calibration of T1w/T2w and T1w/FLAIR ratio maps is imperative to account for the sources of variation described above. The nonlinear calibration methods showed the best reduction of between-subject and within-subject variability. The T1w/T2w and T1w/FLAIR ratio seem to be more sensitive to smaller changes in tissue integrity than MTR. Future work is needed to determine the exact substrate of T1w/FLAIR ratio and to obtain correlations with clinical outcome.
Keywords: Image calibration; Integrity; Multiple sclerosis; T1w/FLAIR ratio; T1w/T2w ratio.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Intensity scaling of conventional brain magnetic resonance images avoiding cerebral reference regions: A systematic review.PLoS One. 2024 Mar 14;19(3):e0298642. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0298642. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38483873 Free PMC article.
-
Automated separation of diffusely abnormal white matter from focal white matter lesions on MRI in multiple sclerosis.Neuroimage. 2020 Jun;213:116690. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2020.116690. Epub 2020 Feb 29. Neuroimage. 2020. PMID: 32119987
-
Characterization of white matter lesions in multiple sclerosis using proton density and T1-relaxation measures.Magn Reson Imaging. 2024 Feb;106:110-118. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2023.12.004. Epub 2023 Dec 23. Magn Reson Imaging. 2024. PMID: 38145698
-
Exploring in vivo multiple sclerosis brain microstructural damage through T1w/T2w ratio: a multicentre study.J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2022 Jul;93(7):741-752. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2022-328908. Epub 2022 May 17. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35580993
-
Standardization of T1w/T2w Ratio Improves Detection of Tissue Damage in Multiple Sclerosis.Front Neurol. 2019 Apr 9;10:334. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2019.00334. eCollection 2019. Front Neurol. 2019. PMID: 31024428 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Relevance of choroid plexus volumes in multiple sclerosis.Fluids Barriers CNS. 2025 May 8;22(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s12987-025-00656-7. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2025. PMID: 40340923 Free PMC article.
-
Approximating R1 and R2: A Quantitative Approach to Clinical Weighted MRI.Hum Brain Mapp. 2024 Dec 15;45(18):e70102. doi: 10.1002/hbm.70102. Hum Brain Mapp. 2024. PMID: 39698763 Free PMC article.
-
"Population-level age effects on the white matter structure subserving cognitive flexibility in the human brain".bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jul 1:2024.08.30.610526. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.30.610526. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40631236 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Exploring factors driving the evolution of chronic lesions in multiple sclerosis using machine learning.Eur Radiol. 2025 Jun 17. doi: 10.1007/s00330-025-11771-2. Online ahead of print. Eur Radiol. 2025. PMID: 40528098
-
Intensity scaling of conventional brain magnetic resonance images avoiding cerebral reference regions: A systematic review.PLoS One. 2024 Mar 14;19(3):e0298642. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0298642. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38483873 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Avants B.B., Tustison N., Song G. Advanced normalization tools (ANTS) Insight J. 2009;2(365):1–35.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

