Efficacy and safety of proton pump inhibitors versus vonoprazan in treatment of erosive esophagitis: A PRISMA-compliant systematic review and network meta-analysis
- PMID: 36451489
- PMCID: PMC9704910
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000031807
Efficacy and safety of proton pump inhibitors versus vonoprazan in treatment of erosive esophagitis: A PRISMA-compliant systematic review and network meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Proton-pump inhibitors (PPIs) and vonoprazan are recommended as first-line therapies for erosive esophagitis (EE). However, it is uncertain how the magnitude of efficacy and safety of first-line therapy, the choice of individual PPIs or vonoprazan in the treatment of EE remains controversial. This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of vonoprazan and PPIs in healing esophageal mucosal injury in patients with EE.
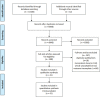
Methods: Relevant databases were searched to collect randomized controlled trials of proton pump inhibitors and vonoprazan in the treatment of reflux esophagitis up to December 2021. Studies on standard-dose PPIs or vonoprazan that were published in Chinese or English and assessed healing effects in EE were included in the analysis. Stata16.0 was used to conduct a network Meta-analysis to evaluate the efficacy and safety of the treatment.
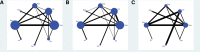
Results: A total of 41 literatures were included with 11,592 enrolled patients. For the endoscopic cure rate, all the PPIs and vonoprazan significantly improve compared to Placebo; Based on the surface under the cumulative ranking curve, Ilaprazole ranked first, followed by esomeprazole, vonoprazan, pantoprazole, lansoprazole, omeprazole, rabeprazole and placebo therapy ranked the last. For the rate of adverse events, there was no significant difference among all the PPIs, vonoprazan, and placebo.
Conclusions: Ilaprazole, esomeprazole and vonoprazan have more advantages in mucosal erosion healing, there was no significant difference in the comparative safety among all interventions.
Copyright © 2022 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

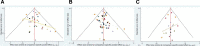
References
-
- Chinese Society of Gastroenterology, Chinese Medical Association. Chinese expert consensus of gastroesophageal reflux disease in China in 2020. Chin J Dig. 2020;40:649–63.
-
- Fass R, Boeckxstaens GE, El-Serag H, et al. Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2021;7:55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

