Practical Issues in the Management of Polycystic Kidney Disease: Blood Pressure and Water Balance
- PMID: 36451711
- PMCID: PMC9685325
- DOI: 10.5049/EBP.2022.20.1.10
Practical Issues in the Management of Polycystic Kidney Disease: Blood Pressure and Water Balance
Abstract
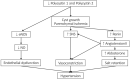
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease is the most common hereditary renal disease affecting more than 13 million people worldwide. Renal function deteriorates as the cysts in both kidneys increase in number and size, which eventually results in end-stage kidney failure. Until recently, conservative management for chronic kidney disease such as blood pressure control, low sodium diet, adequate water intake, and weight control were known for the only treatment of polycystic kidney disease. However, the introduction of disease-modifying drug has led to the new paradigm shift in the management of polycystic kidney disease. Tolvaptan, the vasopressin V2 receptor antagonist, has been introduced to the patients with large kidneys since it can inhibit cyclic adenosine monophosphate, attenuates cyst growth, and delays renal failure. This article reviews the two important practical issues in the management of polycystic kidney disease: blood pressure and water balance. Firstly, the article will review the pathogenesis of high blood pressure in polycystic kidney disease and will demonstrate the current up-to-date management plan for blood pressure control. Secondly, this article will explain the mechanism of Tolvaptan on the treatment of polycystic kidney disease and its possible adverse effect on water and sodium balance.
Keywords: Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease; Blood pressure; Vasopressin V2 receptor antagonist; Water balance.
Copyright © 2022 Korean Society for Electrolyte and Blood Pressure Research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Tolvaptan, a vasopressin V2 receptor antagonist, is the world's first approved drug for treatment of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD)].Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2022;157(4):254-260. doi: 10.1254/fpj.22006. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2022. PMID: 35781456 Japanese.
-
TOLVAPTAN USE IN SEVERE NEONATAL AUTOSOMAL DOMINANT POLYCYSTIC KIDNEY DISEASE (ADPKD): THE PHARMACEUTICAL CHALLENGE.Arch Dis Child. 2016 Sep;101(9):e2. doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2016-311535.61. Arch Dis Child. 2016. PMID: 27540244
-
Rationale and design of the TEMPO (Tolvaptan Efficacy and Safety in Management of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease and its Outcomes) 3-4 Study.Am J Kidney Dis. 2011 May;57(5):692-9. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2010.11.029. Epub 2011 Feb 17. Am J Kidney Dis. 2011. PMID: 21333426 Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical Manifestation and Management of ADPKD in Western Countries.Kidney Dis (Basel). 2016 Oct;2(3):120-127. doi: 10.1159/000449394. Epub 2016 Oct 6. Kidney Dis (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27921039 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vasopressin antagonists in polycystic kidney disease.Semin Nephrol. 2008 May;28(3):306-17. doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2008.03.003. Semin Nephrol. 2008. PMID: 18519091 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease-Related Multifocal Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Narrative Iconographic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 23;26(9):3965. doi: 10.3390/ijms26093965. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362206 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of the L-Arginine-Nitric Oxide Molecular Pathway in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease.J Pers Med. 2024 Mar 11;14(3):299. doi: 10.3390/jpm14030299. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 38541041 Free PMC article.
References
-
- BChurchill DN, Bear JC, Morgan J, Payne RH, McManamon PJ, Gault MH. Prognosis of adult onset polycystic kidney disease re-evaluated. Kidney Int. 1984;26(2):190–193. - PubMed
-
- Dalgaard OZ. Bilateral polycystic disease of the kidneys; a follow-up of two hundred and eighty-four patients and their families. Acta Med Scand Suppl. 1957;328:1–255. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources