Autoantibodies as biomarkers for breast cancer diagnosis and prognosis
- PMID: 36451832
- PMCID: PMC9701846
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1035402
Autoantibodies as biomarkers for breast cancer diagnosis and prognosis
Abstract
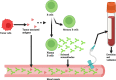
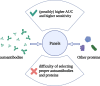
Breast cancer is the most common cancer in women worldwide and is a substantial public health problem. Screening for breast cancer mainly relies on mammography, which leads to false positives and missed diagnoses and is especially non-sensitive for patients with small tumors and dense breasts. The prognosis of breast cancer is mainly classified by tumor, node, and metastasis (TNM) staging, but this method does not consider the molecular characteristics of the tumor. As the product of the immune response to tumor-associated antigens, autoantibodies can be detected in peripheral blood and can be used as noninvasive, presymptomatic, and low-cost biomarkers. Therefore, autoantibodies can provide a possible supplementary method for breast cancer screening and prognosis classification. This article introduces the methods used to detect peripheral blood autoantibodies and the research progress in the screening and prognosis of breast cancer made in recent years to provide a potential direction for the examination and treatment of breast cancer.
Keywords: autoantibody; autoantibody detection; breast cancer; early diagnosis; prognosis.
Copyright © 2022 Yang, Han, Yi and Long.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

