Mechanisms and biomarkers of successful allergen-specific immunotherapy
- PMID: 36452016
- PMCID: PMC9669467
- DOI: 10.5415/apallergy.2022.12.e45
Mechanisms and biomarkers of successful allergen-specific immunotherapy
Abstract
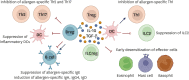
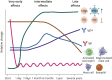
Allergen-specific immunotherapy (AIT) is considered the only curative treatment for allergic diseases mediated by immunoglobulin E (IgE). Currently, the route of administration depends both on the different types of causal allergens and on its effectiveness and safety profile. Several studies have reported the mechanisms and changes in humoral and cellular response underlying AIT; however, the full picture remains unknown. Knowledge of who can benefit from this type of treatment is urgently needed due to the patient safety risks and costs of AIT. In vivo or in vitro biomarkers have become a strategy to predict clinical outcomes in precision medicine. There are currently no standardized biomarkers that allow determining successful responses to AIT, however, some studies have found differences between responders and nonresponders. In addition, different candidates have been postulated that may have the potential to become biomarkers. In this review, we aim to summarize the findings to date related to biomarkers in different IgE-mediated allergic diseases (respiratory, food, and venom allergy) with the potential to define who will benefit from AIT.
Keywords: Allergen-specific immunotherapy; Allergy; Biomarkers; IgE; Regulatory T cells; regulatory B cells.
Copyright © 2022. Asia Pacific Association of Allergy, Asthma and Clinical Immunology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Komlósi ZI, Kovács N, Sokolowska M, van de Veen W, Akdis M, Akdis CA. Mechanisms of subcutaneous and sublingual aeroallergen immunotherapy: what is new? Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2020;40:1–14. - PubMed
-
- Farraia M, Paciência I, Castro Mendes F, Cavaleiro Rufo J, H Shamji M, Agache I, Moreira A. Cost-effectiveness analysis of house dust mite allergen immunotherapy in children with allergic asthma. Allergy. 2022;77:2688–2698. - PubMed
-
- Parra-Padilla D, Zakzuk J, Carrasquilla M, Alvis-Guzmán N, Dennis R, Rojas MX, Rondón M, Pérez A, Peñaranda A, Barragán AM, Caraballo L, García E. Cost-effectiveness of the subcutaneous house dust mite allergen immunotherapy plus pharmacotherapy for allergic asthma: a mathematical model. Allergy. 2021;76:2229–2233. - PubMed
-
- Farraia M, Paciência I, Castro Mendes F, Cavaleiro Rufo J, Shamji M, Agache I, Moreira A. Allergen immunotherapy for asthma prevention: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized and non-randomized controlled studies. Allergy. 2022;77:1719–1735. - PubMed
-
- Senna G, Caminati M, Lockey RF. Allergen immunotherapy adherence in the real world: How bad is it and how can it be improved? Curr Treat Options Allergy. 2015;2:39–53.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
