Enhanced pathogenicity by up-regulation of A20 after avian leukemia subgroup a virus infection
- PMID: 36452148
- PMCID: PMC9702354
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2022.1031480
Enhanced pathogenicity by up-regulation of A20 after avian leukemia subgroup a virus infection
Abstract
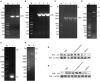
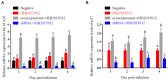
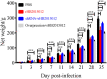
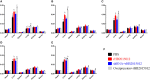
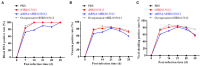
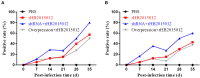
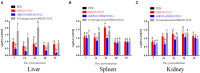
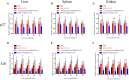
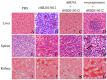
Avian leukemia virus subgroup A (ALV-A) infection slows chicken growth, immunosuppression, and tumor occurrence, causing economic loss to the poultry industry. According to previous findings, A20 has a dual role in promoting and inhibiting tumor formation but has rarely been studied in avians. In this study, A20 overexpression and shRNA interference recombinant adenoviruses were constructed and inoculated into chicken embryos, and ALV-A (rHB2015012) was inoculated into 1-day-old chicks. Analysis of body weight, organ index, detoxification, antibody production, organ toxin load, and Pathological observation revealed that A20 overexpression could enhance ALV-A pathogenicity. This study lays the foundation for subsequent exploration of the A20-mediated tumorigenic mechanism of ALV-A.
Keywords: A20; ALV-A; chicken; pathogenic; recombinant adenovirus.
Copyright © 2022 Chen, Wang, Yang, Fang, Liu, Liang and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Cui Z, Sun SH. Prevalence situation and prevention and control of avian leukosis. Chin J Vet Drug. (2009) 43:37–41.
-
- Relova D, Merino A. Avian leukosis virus subtype A and subtype J in different flocks with tumor disease. Rev Salud Anim. (2013) 35:70.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

