One-year recurrence of stroke and death in Lebanese survivors of first-ever stroke: Time-to-Event analysis
- PMID: 36452174
- PMCID: PMC9702576
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2022.973200
One-year recurrence of stroke and death in Lebanese survivors of first-ever stroke: Time-to-Event analysis
Abstract
Background: To date, despite the application of secondary prevention worldwide, first-ever stroke survivors remain at imminent risk of stroke recurrence and death in the short and long term. The present study aimed to assess the cumulative risk rates and identify baseline differences and stroke characteristics of Lebanese survivors.
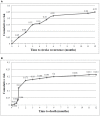
Methods: A prospective longitudinal study was conducted among survivors ≥18 years old who were followed-up for 15 months through a face-to-face interview. Kaplan-Meier method was used to calculate the cumulative rates of stroke mortality and recurrence. Cox-regression univariate and multivariable analyses were performed to identify the predictors of both outcomes.
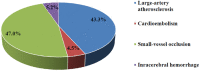
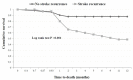
Results: Among 150 subjects (mean age 74 ± 12 years; 58.7% men vs. 44.3% women; 95.3% with ischemic stroke vs. 4.3% with intracerebral hemorrhage), high cumulative risk rates of stroke recurrence (25%) and death (21%) were highlighted, especially in the acute phase. Survival rates were lesser in patients with stroke recurrence compared to those without recurrence (Log rank test p < 0.001). Older age was the main predictor for both outcomes (p < 0.02). Large artery atherosclerosis was predominant in patients with stroke recurrence and death compared to small vessel occlusion (p < 0.02). Higher mental component summary scores of quality of life were inversely associated with stroke recurrence (p < 0.01). Lebanese survivors exhibited the highest percentages of depression and anxiety; elevated Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS) scores were seen in those with stroke recurrence and those who died (≥80% with mean HADS scores ≥8). Lower Mini-Mental State Examination scores at the acute phase increased the risk of both outcomes by 10% (p < 0.03). Three out of 13 mortalities (23.1%) were presented with early epileptic seizures (p = 0.012). High educational level was the protective factor against stroke recurrence (p = 0.019). Administration of intravenous thrombolysis decreased the risk of both outcomes by 10% (p > 0.05).
Conclusion: Higher rates of stroke recurrence and death were observed in the first year following a stroke in Lebanon. Various factors were identified as significant determinants. Thus, health care providers and officials in Lebanon can use these findings to implement effective preventive strategies to best address the management of these factors to reduce the stroke burden and improve the short and long-term prognosis of stroke survivors.
Keywords: Lebanon; burden; cumulative risk rate; death; factors; recurrence; stroke; survivors.
Copyright © 2022 Boutros, Khazaal, Taliani, Said Sadier, Salameh and Hosseini.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Factors associated with cognitive impairment at 3, 6, and 12 months after the first stroke among Lebanese survivors.Brain Behav. 2023 Jan;13(1):e2837. doi: 10.1002/brb3.2837. Epub 2022 Dec 10. Brain Behav. 2023. PMID: 36495111 Free PMC article.
-
Three-year survival and recurrence after first-ever stroke: the Joinville stroke registry.BMC Neurol. 2015 May 1;15:70. doi: 10.1186/s12883-015-0317-1. BMC Neurol. 2015. PMID: 25927467 Free PMC article.
-
Pediatric stroke among Hong Kong Chinese subjects.Pediatrics. 2004 Aug;114(2):e206-12. doi: 10.1542/peds.114.2.e206. Pediatrics. 2004. PMID: 15286258
-
Mortality and Predictors of Death Poststroke: Data from a Multicenter Prospective Cohort of Lebanese Stroke Patients.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2019 Apr;28(4):859-868. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2018.11.033. Epub 2019 Jan 10. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2019. PMID: 30638943
-
Long-term neurological, vascular, and mortality outcomes after stroke.Int J Stroke. 2018 Oct;13(8):787-796. doi: 10.1177/1747493018798526. Epub 2018 Aug 30. Int J Stroke. 2018. PMID: 30160619 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects and central mechanism of electroacupuncture and MRI-navigated rTMS for PSD: study protocol for an fMRI-based single-center, randomized, controlled, open-label trial.Front Psychiatry. 2024 Jan 4;14:1226777. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1226777. eCollection 2023. Front Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38250275 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of depression on stroke outcomes among stroke survivors: Systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2023 Dec 1;18(12):e0294668. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0294668. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 38039323 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rahayu LP, Sudrajat DA, Nurdina G, Agustina EN, Putri TARK. The risk factor of recurrence stroke among stroke and transient ischemic attack patients in Indonesia. KnE Life Sci. (2019) 87–97. 10.18502/kls.v4i13.5229 - DOI
-
- WHO . Stroke, Cerebrovascular Accident (2021). Available online at: https://www.emro.who.int/health-topics/stroke-cerebrovascular-accident/i... (accessed February 25, 2021).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

