Advanced technologies for quantum photonic devices based on epitaxial quantum dots
- PMID: 36452403
- PMCID: PMC9706462
- DOI: 10.1002/qute.201900034
Advanced technologies for quantum photonic devices based on epitaxial quantum dots
Abstract
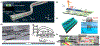
Quantum photonic devices are candidates for realizing practical quantum computers and networks. The development of integrated quantum photonic devices can greatly benefit from the ability to incorporate different types of materials with complementary, superior optical or electrical properties on a single chip. Semiconductor quantum dots (QDs) serve as a core element in the emerging modern photonic quantum technologies by allowing on-demand generation of single-photons and entangled photon pairs. During each excitation cycle, there is one and only one emitted photon or photon pair. QD photonic devices are on the verge of unfolding for advanced quantum technology applications. In this review, we focus on the latest significant progress of QD photonic devices. We first discuss advanced technologies in QD growth, with special attention to droplet epitaxy and site-controlled QDs. Then we overview the wavelength engineering of QDs via strain tuning and quantum frequency conversion techniques. We extend our discussion to advanced optical excitation techniques recently developed for achieving the desired emission properties of QDs. Finally, the advances in heterogeneous integration of active quantum light-emitting devices and passive integrated photonic circuits are reviewed, in the context of realizing scalable quantum information processing chips.
Keywords: epitaxial growth technology; heterogeneous photonic integration; quantum dot; quantum photonic device; wavelength tuning.
Figures




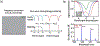
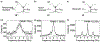
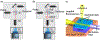



References
-
- O’Brien JL, Furusawa A, Vučkovič J, Nat. Photonics 2009, 3, 687.
-
- Knill E, Laflamme R, Milburn GJ, Nature 2001, 409, 46. - PubMed
-
- O’Brien JL, Science 2007, 318, 1567. - PubMed
-
- Gisin N, Thew R, Nat. Photonics 2007, 1, 165.
-
- Schmitt-Manderbach T, Weier H, Fürst M, Ursin R, Tiefenbacher F, Scheidl T, Perdigues J, Sodnik Z, Kurtsiefer C, Rarity JG, Zeilinger A, Weinfurter H, Phys. Rev. Lett 2007, 98, 010504. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
