The global research of bladder cancer immunotherapy from 2012 to 2021: A bibliometric analysis
- PMID: 36452503
- PMCID: PMC9703076
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.999203
The global research of bladder cancer immunotherapy from 2012 to 2021: A bibliometric analysis
Abstract
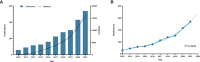
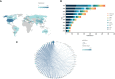
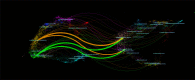
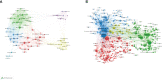
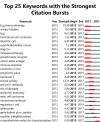
Intravesical instillation of Bacillus Calmette-Guérin has been used as an immunotherapy to treat superficial bladder cancer for almost half a century. In recent years, the approval of several monoclonal antibody treatments has transformed the treatment landscape for patients with muscle-invasive or metastatic uroepithelial carcinoma. The purpose of this study was to conduct a thorough review of immunotherapy in bladder cancer through a bibliometric approach. Publications related to bladder cancer immunotherapy were obtained from the Web of Science Core Collection on July 1st, 2022. We conducted a bibliometric analysis of literature information using CiteSpace IV, VOSviewer, and Scimago Graphica, including co-authorship or co-citation of authors, countries/regions, journals, references, and keyword co-occurrence. There was a total of 2,352 papers included, with the most contributions coming from the United States, China, and Italy. The United States had the highest H-index value and was the leading country in this field. Meanwhile, the number of publications in China was steadily growing. The top three productive researchers were Kamat AM, Necchi A, and Shariat SF, with Powles T as the top co-cited author. Most papers were published by the University of Texas System. The majority of papers in this field were published in Urologic Oncology Seminars and Original Investigations and European Urology was the most influential journal with the highest H-index. The tumor microenvironment and complete molecular characterization may still be the frontier in this research area, allowing us to obtain a better understanding of the pathogenesis and clinical prognosis of bladder cancer. More research are conducted to identify clinically meaningful biomarkers that may provide opportunities for the personalization of bladder cancer therapy. This study provides clinicians and researchers with an overview and helpful guidance on how to choose the research direction and management of bladder cancer immunotherapy.
Keywords: bibliometrics; bladder cancer; immune checkpoint inhibitor; immunotherapy; metastatic urothelial carcinoma.
Copyright © 2022 Qiu, Deng, Li, Qiu, Shen and Ding.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A bibliometric insight into neoadjuvant chemotherapy in bladder cancer: trends, collaborations, and future avenues.Front Immunol. 2024 Feb 19;15:1297542. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1297542. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38444854 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging trends of BCG immunotherapy for bladder cancer in last decade: a bibliometric and visualization analysis.Front Oncol. 2023 Apr 14;13:1092969. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1092969. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37124495 Free PMC article.
-
Bibliometric study of immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Immunol. 2023 Aug 4;14:1210802. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1210802. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37600802 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Knowledge-map analysis of bladder cancer immunotherapy.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2023 Dec 15;19(3):2267301. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2023.2267301. Epub 2023 Oct 30. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2023. PMID: 37903500 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Global research trends and hotspots on imaging of bladder cancer: A bibliometric and visual analysis from 1981 to 2023.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Mar 21;104(12):e41907. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000041907. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40128048 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A scientometric review of the growing trends in transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS).Front Hum Neurosci. 2024 Mar 6;18:1362593. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2024.1362593. eCollection 2024. Front Hum Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38510513 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Astragalus polysaccharide inhibits the development of urothelial carcinoma by activating AMPK signaling to induce BENC1-xCT complex formation.Aging (Albany NY). 2023 Sep 20;15(18):9438-9452. doi: 10.18632/aging.205007. Epub 2023 Sep 20. Aging (Albany NY). 2023. PMID: 37733667 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammation-related research within the field of bladder cancer: a bibliometric analysis.Front Oncol. 2023 Jun 7;13:1126897. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1126897. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37350946 Free PMC article.
-
A bibliometric insight into neoadjuvant chemotherapy in bladder cancer: trends, collaborations, and future avenues.Front Immunol. 2024 Feb 19;15:1297542. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1297542. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38444854 Free PMC article.
-
Emergent trends in organ-on-a-chip applications for investigating metastasis within tumor microenvironment: A comprehensive bibliometric analysis.Heliyon. 2023 Dec 9;10(1):e23504. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23504. eCollection 2024 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38187238 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nadal R, Bellmunt J. Management of metastatic bladder cancer. Cancer Treat Rev (2019) 76:10–21. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

