Endoscopic Modified Denker's Approach for the Treatment of Juvenile Nasopharyngeal Angiofibroma
- PMID: 36452834
- PMCID: PMC9702475
- DOI: 10.1007/s12070-020-01984-w
Endoscopic Modified Denker's Approach for the Treatment of Juvenile Nasopharyngeal Angiofibroma
Abstract
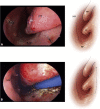
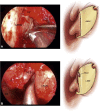
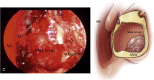
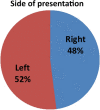
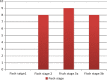
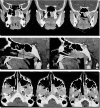
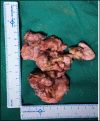
Juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma is a benign vascular lesion with propensity of bony erosion leading to skull base involvement and intracranial extension. It involves multiple compartments which are difficult to access surgically. With surgical expertise endoscopic resection of angiofibroma has become the preferred choice of surgical management. This article presents our experience with endoscopic approach for angiofibroma and establishes the modified Denker's procedure as a effective approach for removal of tumor. A prospective case study was done on 25 cases of juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma treated surgically by endonasal endoscopic modified Denker's approach in the department of ENT at BJ Medical College, Ahmedabad over a period of 4 years from January 2015 to January 2019. This technique was used up to Fisch stage 3b with extension up to infratemporal fossa. Using this technique no major recurrence or major morbidity was observed and did not produce any late serious complications. The endoscopic technique allows the surgeon to achieve an extensive exposure of the sinuses and control of the sphenopalatine and internal maxillary arteries without the risk of palatal dysfunction, oronasal fistula, or facial scarring. In addition, the modified Denkers approach can be an effective and less mutilating technique in managing recurrences.
Keywords: Angiofibroma; Endoscopic; Modified Denker’s.
© Association of Otolaryngologists of India 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declares that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Conley J, Healey WV, Blaugrund SM, Erzin KH. Nasopharyngeal angiofibroma in the juvenile. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1968;126(4):825–837. - PubMed
-
- Batsakis JG (1979) Tumors of the head and neck: clinical and pathological considerations. Williams & Wilkins
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
