Isolated Laryngeal Tuberculosis: a Diagnostic Dilemma
- PMID: 36452854
- PMCID: PMC9702101
- DOI: 10.1007/s12070-020-02139-7
Isolated Laryngeal Tuberculosis: a Diagnostic Dilemma
Abstract
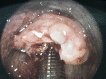
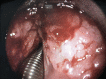
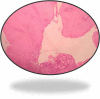
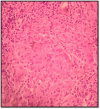
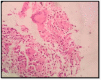
Laryngeal tuberculosis is a rare condition, isolated laryngeal tuberculosis without pulmonary manifestations is even more rare. Patients usually presents with voice change, difficulty in swallowing and other constitutional symptoms. The symptoms and findings can look like malignancy in most of the cases. Here, we present a case of primary laryngeal tuberculosis without pulmonary tuberculosis. A 24 year old man who presented to us with hoarseness of voice with 1 year duration. Laryngoscopic study showed a proliferative growth in the epiglottis, aryepiglottic folds and vocal cords and was diagnosed to have laryngeal tuberculosis on histopathology by the typical appearance of granuloma and caseous necrosis. The patient was started on standard antitubercular therapy and he had an excellent response to the same within 6 months. Isolated laryngeal tuberculosis should be suspected in patients with laryngeal complaints with no pulmonary symptoms, especially in a developing country like India where pulmonary tuberculosis is prevalent. Even though isolated laryngeal tuberculosis cases are rare, we should keep in mind the possibility of tuberculosis in the differential diagnosis of laryngeal tumors, as the incidence of tuberculosis is steadily increasing.
Keywords: Anti tubercular drugs; Larynx; Primary; Tuberculosis.
© Association of Otolaryngologists of India 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Laryngeal tuberculosis without pulmonary involvement.Caspian J Intern Med. 2012 Winter;3(1):397-9. Caspian J Intern Med. 2012. PMID: 26557293 Free PMC article.
-
Laryngeal tuberculosis: a neglected diagnosis.BMJ Case Rep. 2022 Feb 7;15(2):e248095. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2021-248095. BMJ Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 35131802 Free PMC article.
-
Rare causes of voice hoarseness: a case report.Nepal Med Coll J. 2008 Jun;10(2):141-3. Nepal Med Coll J. 2008. PMID: 18828442
-
Epiglottic tuberculosis: differential diagnosis and treatment. Case report and review of the literature.Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2001 Feb;110(2):197-201. doi: 10.1177/000348940111000218. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2001. PMID: 11219530 Review.
-
Laryngeal tubercolosis: a case report with focus on voice assessment and review of the literature.Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2022 Oct;42(5):407-414. doi: 10.14639/0392-100X-N2091. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2022. PMID: 36541378 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Isolated laryngeal tuberculosis: A diagnostic dilemma.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2024 Mar;116:109376. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2024.109376. Epub 2024 Feb 10. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 38350377 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
