Normalization benchmark of ATAC-seq datasets shows the importance of accounting for GC-content effects
- PMID: 36452861
- PMCID: PMC9701614
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crmeth.2022.100321
Normalization benchmark of ATAC-seq datasets shows the importance of accounting for GC-content effects
Abstract
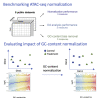
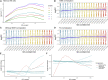
The assay for transposase-accessible chromatin using sequencing (ATAC-seq) allows the study of epigenetic regulation of gene expression by assessing chromatin configuration for an entire genome. Despite its popularity, there have been limited studies investigating the analytical challenges related to ATAC-seq data, with most studies leveraging tools developed for bulk transcriptome sequencing. Here, we show that GC-content effects are omnipresent in ATAC-seq datasets. Since the GC-content effects are sample specific, they can bias downstream analyses such as clustering and differential accessibility analysis. We introduce a normalization method based on smooth-quantile normalization within GC-content bins and evaluate it together with 11 different normalization procedures on 8 public ATAC-seq datasets. Accounting for GC-content effects in the normalization is crucial for common downstream ATAC-seq data analyses, improving accuracy and interpretability. Through case studies, we show that exploratory data analysis is essential to guide the choice of an appropriate normalization method for a given dataset.
Keywords: ATAC-seq; GC-content; clustering; differential accessibility; epigenetics; normalization.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Aird D., Ross M.G., Chen W.-S., Danielsson M., Fennell T., Russ C., Jaffe D.B., Nusbaum C., Gnirke A. Analyzing and minimizing PCR amplification bias in Illumina sequencing libraries. Genome Biol. 2011;12:R18. https://genomebiology.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/gb-2011-12-2-r18 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andersson R., Gebhard C., Miguel-Escalada I., Hoof I., Bornholdt J., Boyd M., Chen Y., Zhao X., Schmidl C., Suzuki T., et al. An atlas of active enhancers across human cell types and tissues. Nature. 2014;507:455–461. https://www.nature.com/articles/nature12787 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Benjamini Y., Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. Roy. Stat. Soc. B. 1995;57:289–300. https://www.jstor.org/stable/2346101?seq=1#page_scan_tab_contents
-
- Benjamini Y., Speed T.P. Summarizing and correcting the GC content bias in high-throughput sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40:e72. https://academic.oup.com/nar/article/40/10/e72/2411059 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bolstad B.M., Irizarry R.A., Astrand M., Speed T.P. A comparison of normalization methods for high density oligonucleotide array data based on variance and bias. Bioinformatics. 2003;19:185–193. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12538238 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

