Leukoencephalopathy, calcifications, and cysts: Labrune syndrome
- PMID: 36452891
- PMCID: PMC9703455
- DOI: 10.1016/j.radcr.2022.11.026
Leukoencephalopathy, calcifications, and cysts: Labrune syndrome
Abstract
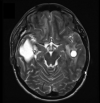
Labrune syndrome is an extremely rare disorder characterized by a radiological triad of leukoencephalopathy, cerebral calcifications, and cysts. The condition is the result of an autosomal mutation in the SNORD118 gene, a non-protein encoding gene that mediates rRNA synthesis. The mutation results selectively in cerebral microangiopathy through an unknown mechanism. Radiological imaging is central to diagnosing the condition, but, because the condition is so rare, there is no standard treatment paradigm. We describe the longitudinal progression of a case of Labrune syndrome, including the radiological diagnosis and imaging and surgical management.
Keywords: Cerebral calcifications; Cerebral cysts; Leukoencephalopathy; Microangiopathy; Ribosomopathy; White matter.
© 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. on behalf of University of Washington.
Figures
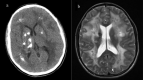
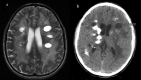
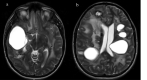
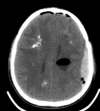


References
-
- Labrune P, Lacroix C, Goutières F, de Laveaucoupet J, Chevalier P, Zerah M, et al. Extensive brain calcifications, leukodystrophy, and formation of parenchymal cysts: a new progressive disorder due to diffuse cerebral microangiopathy. Neurology. 1996;46(5):1297–1301. - PubMed
-
- Wang M, Zhang M, Wu L, Dong Z, Yu S. Leukoencephalopathy with cerebral calcification and cysts: cases report and literature review. J Neurol Sci. 2016;370:173–179. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

