Promotion of Lung Cancer Metastasis by SIRT2-Mediated Extracellular Protein Deacetylation
- PMID: 36453571
- PMCID: PMC9875677
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202205462
Promotion of Lung Cancer Metastasis by SIRT2-Mediated Extracellular Protein Deacetylation
Abstract
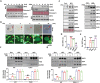
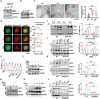
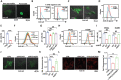
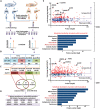
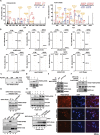
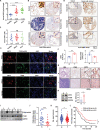
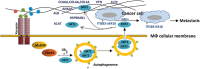
Acetylation of extracellular proteins has been observed in many independent studies where particular attention has been given to the dynamic change of the microenvironmental protein post-translational modifications. While extracellular proteins can be acetylated within the cells prior to their micro-environmental distribution, their deacetylation in a tumor microenvironment remains elusive. Here it is described that multiple acetyl-vWA domain-carrying proteins including integrin β3 (ITGB3) and collagen 6A (COL6A) are deacetylated by Sirtuin family member SIRT2 in extracellular space. SIRT2 is secreted by macrophages following toll-like receptor (TLR) family member TLR4 or TLR2 activation. TLR-activated SIRT2 undergoes autophagosome translocation. TNF receptor associated factor 6 (TRAF6)-mediated autophagy flux in response to TLR2/4 activation can then pump SIRT2 into the microenvironment to function as extracellular SIRT2 (eSIRT2). In the extracellular space, eSIRT2 deacetylates ITGB3 on aK416 involved in cell attachment and migration, leading to a promotion of cancer cell metastasis. In lung cancer patients, significantly increased serum eSIRT2 level correlates with dramatically decreased ITGB3-K416 acetylation in cancer cells. Thus, the extracellular space is a subcellular organelle-like arena where eSIRT2 promotes cancer cell metastasis via catalyzing extracellular protein deacetylation.
Keywords: SIRT2; acetylation; lung cancer; metastasis; secretion.
© 2022 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82030077/China Natural Science Foundation
- 81820108023/China Natural Science Foundation
- U1603284/China Natural Science Foundation
- 216YFC1302402/China Ministry of Science and Technology
- 2018YFC1705505/China Ministry of Science and Technology
- Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions
- Q424900220/Soochow University Research Development Fund
- 31801058/Soochow University Research Development Fund
- 81902977/Soochow University Research Development Fund
- 216YFC1302402/Ministry of Science and Technology of the People's Republic of China
- 2018YFC1705505/Ministry of Science and Technology of the People's Republic of China
- Z23H160028/Zhejiang Provincail Natural Science Foundation of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
