Electroactive Biomaterials for Facilitating Bone Defect Repair under Pathological Conditions
- PMID: 36453574
- PMCID: PMC9839869
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202204502
Electroactive Biomaterials for Facilitating Bone Defect Repair under Pathological Conditions
Abstract
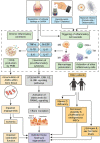
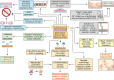
Bone degeneration associated with various diseases is increasing due to rapid aging, sedentary lifestyles, and unhealthy diets. Living bone tissue has bioelectric properties critical to bone remodeling, and bone degeneration under various pathological conditions results in significant changes to these bioelectric properties. There is growing interest in utilizing biomimetic electroactive biomaterials that recapitulate the natural electrophysiological microenvironment of healthy bone tissue to promote bone repair. This review first summarizes the etiology of degenerative bone conditions associated with various diseases such as type II diabetes, osteoporosis, periodontitis, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, osteomyelitis, and metastatic osteolysis. Next, the diverse array of natural and synthetic electroactive biomaterials with therapeutic potential are discussed. Putative mechanistic pathways by which electroactive biomaterials can mitigate bone degeneration are critically examined, including the enhancement of osteogenesis and angiogenesis, suppression of inflammation and osteoclastogenesis, as well as their anti-bacterial effects. Finally, the limited research on utilization of electroactive biomaterials in the treatment of bone degeneration associated with the aforementioned diseases are examined. Previous studies have mostly focused on using electroactive biomaterials to treat bone traumatic injuries. It is hoped that this review will encourage more research efforts on the use of electroactive biomaterials for treating degenerative bone conditions.
Keywords: biomaterials; bone; degenerative; disease; electric; scaffold.
© 2022 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2021YFB3800800/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2021YFC2400400/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 82022016/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 51973004/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81991505/National Natural Science Foundation of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
