A long-read and short-read transcriptomics approach provides the first high-quality reference transcriptome and genome annotation for Pseudotsuga menziesii (Douglas-fir)
- PMID: 36454025
- PMCID: PMC10468028
- DOI: 10.1093/g3journal/jkac304
A long-read and short-read transcriptomics approach provides the first high-quality reference transcriptome and genome annotation for Pseudotsuga menziesii (Douglas-fir)
Abstract
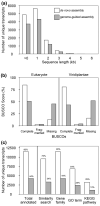
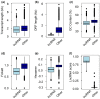
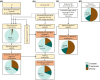
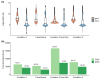
Douglas-fir (Pseudotsuga menziesii) is native to western North America. It grows in a wide range of environmental conditions and is an important timber tree. Although there are several studies on the gene expression responses of Douglas-fir to abiotic cues, the absence of high-quality transcriptome and genome data is a barrier to further investigation. Like for most conifers, the available transcriptome and genome reference dataset for Douglas-fir remains fragmented and requires refinement. We aimed to generate a highly accurate, and complete reference transcriptome and genome annotation. We deep-sequenced the transcriptome of Douglas-fir needles from seedlings that were grown under nonstress control conditions or a combination of heat and drought stress conditions using long-read (LR) and short-read (SR) sequencing platforms. We used 2 computational approaches, namely de novo and genome-guided LR transcriptome assembly. Using the LR de novo assembly, we identified 1.3X more high-quality transcripts, 1.85X more "complete" genes, and 2.7X more functionally annotated genes compared to the genome-guided assembly approach. We predicted 666 long noncoding RNAs and 12,778 unique protein-coding transcripts including 2,016 putative transcription factors. We leveraged the LR de novo assembled transcriptome with paired-end SR and a published single-end SR transcriptome to generate an improved genome annotation. This was conducted with BRAKER2 and refined based on functional annotation, repetitive content, and transcriptome alignment. This high-quality genome annotation has 51,419 unique gene models derived from 322,631 initial predictions. Overall, our informatics approach provides a new reference Douglas-fir transcriptome assembly and genome annotation with considerably improved completeness and functional annotation.
Keywords: Pseudotsuga menziesii var. glauca; Pseudotsuga menziesii var. menziesii; de novo assembly; NovaSeq; PacBio Iso-Seq; coastal Douglas-fir; full-length isoform; functional annotation; genome annotation; interior Douglas-fir; long noncoding RNA; reference transcriptome; transcription factors.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Genetics Society of America.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest None declared.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A SNP resource for Douglas-fir: de novo transcriptome assembly and SNP detection and validation.BMC Genomics. 2013 Feb 28;14:137. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-137. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23445355 Free PMC article.
-
A catalogue of putative unique transcripts from Douglas-fir (Pseudotsuga menziesii) based on 454 transcriptome sequencing of genetically diverse, drought stressed seedlings.BMC Genomics. 2012 Nov 28;13:673. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-673. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 23190494 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription through the eye of a needle: daily and annual cyclic gene expression variation in Douglas-fir needles.BMC Genomics. 2017 Jul 24;18(1):558. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-3916-y. BMC Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28738815 Free PMC article.
-
Ectomycorrhizal fungi associated with ponderosa pine and Douglas-fir: a comparison of species richness in native western North American forests and Patagonian plantations from Argentina.Mycorrhiza. 2007 Jul;17(5):355-373. doi: 10.1007/s00572-007-0121-x. Epub 2007 Mar 8. Mycorrhiza. 2007. PMID: 17345105 Review.
-
De novo assembly of transcriptomes and differential gene expression analysis using short-read data from emerging model organisms - a brief guide.Front Zool. 2024 Jun 20;21(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s12983-024-00538-y. Front Zool. 2024. PMID: 38902827 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Uncovering epigenetic and transcriptional regulation of growth in Douglas-fir: identification of differential methylation regions in mega-sized introns.Plant Biotechnol J. 2024 Apr;22(4):863-875. doi: 10.1111/pbi.14229. Epub 2023 Nov 20. Plant Biotechnol J. 2024. PMID: 37984804 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bayega A, Fahiminiya S, Oikonomopoulos S, Ragoussis J. 2018. Current and future methods for mRNA analysis: a drive toward single molecule sequencing. In: Raghavachari N, Garcia-Reyero N, editors. Gene Expression Analysis: Methods and Protocols, Methods in Molecular Biology. New York: (NY: ): Springer. p. 209–241. - PubMed
-
- Bedon F, Bomal C, Caron S, Levasseur C, Boyle B, Mansfield SD, Schmidt A, Gershenzon J, Grima-Pettenati J, Séguin A. Subgroup 4 R2R3-MYBs in conifer trees: gene family expansion and contribution to the isoprenoid- and flavonoid-oriented responses. J Exp Bot. 2010;61(14):3847–3864. doi:10.1093/jxb/erq196 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
