Long-term analysis of chronic pain associated with lower extremity injuries
- PMID: 36454306
- PMCID: PMC10293374
- DOI: 10.1007/s00402-022-04717-6
Long-term analysis of chronic pain associated with lower extremity injuries
Abstract
Introduction: The main objective of this study is to examine chronic pain and limping in relation to lower extremity and pelvic fracture location in addition to fracture combinations if multiple fractures are present on the same leg that have not been previously reported. We hypothesize that fracture pattern and location of lower extremity and pelvis fractures of multiple injured patients influence their long-term pain outcome.
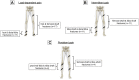
Materials and methods: Retrospective cohort study. Patients with treated multiple lower limb and pelvic fractures at a level 1 trauma center and followed up for at least 10 years postinjury were assessed. Lower leg pain subdivided into persistent, load-dependent and intermittent pain, as well as limping were recorded by using self-administered patient questionnaires and standardized physical examinations performed by a trauma surgeon. Descriptive statistics were used to present comparative measurements between groups.
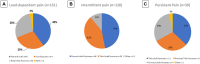
Results: Fifty-seven percent of patients (n = 301) showed chronic lower limb pain 10 years postinjury. Ten percent of all patients with chronic pain displayed persistent pain, and here the most common fracture combination was tibial shaft fractures in combination with femoral shaft or proximal tibial fractures (13%). One hundred fifty-one patients reported load-dependent pain, with the most common fracture combinations being fractures of the foot in combination with femoral shaft fractures or distal tibial fractures (11%). One hundred twenty patients reported intermittent pain, with the most common fracture combinations involving the shaft of the tibia with either the femoral shaft or distal tibia (9%). Two hundred fifteen patients showed a persistent limp, and here the most common fractures were fractures of the femoral shaft (19%), tibial shaft (17%), and pelvis (15%).
Conclusions: In multiple injured patients with lower extremity injuries, the combination of fractures and their location are critical factors in long-term outcome. Patients with chronic persistent or load-dependent pain often had underlying femoral shaft fractures in combination with joint fractures.
Keywords: Acetabulum; Chronic pain; Long-term outcome; Lower limb; Multiple injuries; Polytrauma.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Falkenberg L, Zeckey C, Mommsen P, Winkelmann M, Zelle BA, Panzica M, Pape HC, Krettek C, Probst C. Long-term outcome in 324 polytrauma patients: what factors are associated with posttraumatic stress disorder and depressive disorder symptoms? Eur J Med Res. 2017;22:44. doi: 10.1186/s40001-017-0282-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Seekamp A, Regel G, Bauch S, Takacs J, Tscherne H. Long-term results of therapy of polytrauma patients with special reference to serial fractures of the lower extremity. Unfallchirurg. 1994;97:57–63. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

