Culture impact on the transcriptomic programs of primary and iPSC-derived human alveolar type 2 cells
- PMID: 36454643
- PMCID: PMC9870086
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.158937
Culture impact on the transcriptomic programs of primary and iPSC-derived human alveolar type 2 cells
Abstract
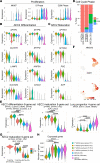
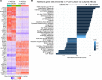
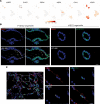
Dysfunction of alveolar epithelial type 2 cells (AEC2s), the facultative progenitors of lung alveoli, is implicated in pulmonary disease pathogenesis, highlighting the importance of human in vitro models. However, AEC2-like cells in culture have yet to be directly compared to their in vivo counterparts at single-cell resolution. Here, we performed head-to-head comparisons among the transcriptomes of primary (1°) adult human AEC2s, their cultured progeny, and human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived AEC2s (iAEC2s). We found each population occupied a distinct transcriptomic space with cultured AEC2s (1° and iAEC2s) exhibiting similarities to and differences from freshly purified 1° cells. Across each cell type, we found an inverse relationship between proliferative and maturation states, with preculture 1° AEC2s being most quiescent/mature and iAEC2s being most proliferative/least mature. Cultures of either type of human AEC2s did not generate detectable alveolar type 1 cells in these defined conditions; however, a subset of iAEC2s cocultured with fibroblasts acquired a transitional cell state described in mice and humans to arise during fibrosis or following injury. Hence, we provide direct comparisons of the transcriptomic programs of 1° and engineered AEC2s, 2 in vitro models that can be harnessed to study human lung health and disease.
Keywords: Human stem cells; Molecular biology; Pulmonology; Stem cells; iPS cells.
Figures





References
-
- Borok Z, et al. Modulation of t1alpha expression with alveolar epithelial cell phenotype in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1998;275(1):L155–L164. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U01 TR001810/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL152970/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007035/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL134745/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL125821/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL145408/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES013508/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL108793/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX001176/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- R01 HL095993/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 HL150876/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL134766/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL148692/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL132266/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001430/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

