Brimonidine and timolol concentrations in the human vitreous and aqueous humors after topical instillation of a 0.1% brimonidine tartrate and 0.5% timolol fixed-combination ophthalmic solution: An interventional study
- PMID: 36454807
- PMCID: PMC9714730
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0277313
Brimonidine and timolol concentrations in the human vitreous and aqueous humors after topical instillation of a 0.1% brimonidine tartrate and 0.5% timolol fixed-combination ophthalmic solution: An interventional study
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the concentrations of brimonidine and timolol in the vitreous and aqueous humors after instillation of a 0.1% brimonidine tartrate and 0.5% timolol fixed-combination ophthalmic solution.
Methods: This single-arm open-label interventional study included patients with macular holes or idiopathic epiretinal membranes who were scheduled for vitrectomy. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants. A 0.1% brimonidine tartrate and 0.5% timolol fixed-combination ophthalmic solution was administered topically twice daily for 1 week preoperatively. The vitreous and aqueous humors were sampled before vitrectomy, and brimonidine and timolol concentrations were quantified using liquid chromatography-tandem spectrometry. This study was registered with the Japan Registry of Clinical Trials (jRCT, ID jRCTs051200008; date of access and registration: April 28, 2020). The study protocol was approved by the University of Fukui Certified Review Board (CRB) and complied with the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki.
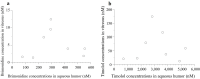
Results: Eight eyes of eight patients (7 phakic eyes and 1 pseudophakic eye) were included in this study. The mean brimonidine concentrations in the vitreous and aqueous humors were 5.04 ± 4.08 nM and 324 ± 172 nM, respectively. Five of the eight patients had brimonidine concentrations >2 nM in the vitreous humor, which is necessary to activate α2 receptors. The mean timolol concentrations in the vitreous and aqueous humors were 65.6 ± 56.0 nM and 3,160 ± 1,570 nM, respectively. Brimonidine concentrations showed significant positive correlations with timolol concentrations in the vitreous humor (P < 0.0001, R2 = 0.97) and aqueous humor (P < 0.0001, R2 = 0.96).
Conclusions: The majority of patients who received a 0.1% brimonidine tartrate and 0.5% timolol topical fixed-combination ophthalmic solution showed a brimonidine concentration >2 nM in the vitreous humor. Brimonidine and timolol may be distributed in the ocular tissues through an identical pathway after topical instillation.
Copyright: © 2022 Orii et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have read the journal’s policy and have the following competing interests: MI, EK, and AM are paid employees of Senju Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials. There are no patents, products in development or marketed products associated with this research to declare.
Figures




References
-
- Quigley H. A., Addicks E. M., Green W. R., “Optic Nerve Damage in Human Glaucoma II. The Site of Injury and Susceptibility to Damage.,” Arch Ophthalmol., 99(4):635–649, 1981. - PubMed
-
- Kass M.A., Heuer D. K., Higginbotham E. J., “The Ocular Hypertension Treatment Study: a randomized trial determines that topical ocular hypotensive medication delays or prevents the onset of primary open-angle glaucoma.,” Arch Ophthalmol., 120(6):701–13; discussion 829–30, 2002. doi: 10.1001/archopht.120.6.701 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

