Association between the Big Five personality traits and medication adherence in patients with cardiovascular disease: A cross-sectional study
- PMID: 36454925
- PMCID: PMC9714849
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0278534
Association between the Big Five personality traits and medication adherence in patients with cardiovascular disease: A cross-sectional study
Abstract
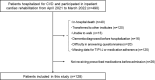
The correlation between personality traits and health outcomes of primary prevention has been examined. However, there is a lack of evidence on the association between the assessment of personality traits and medication adherence for secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease. Thus, this study aimed to explore the association between personality traits and medication adherence, including compliance to prescribed medications and attitudes toward taking medications among patients with cardiovascular disease. This cross-sectional study included patients hospitalized for cardiovascular disease. We assessed the Big Five personality traits (conscientiousness, neuroticism, openness, extraversion, and agreeableness) of each patient at discharge using the Ten-Item Personality Inventory. In addition, we evaluated four aspects of medication adherence using a 12-item version of the medication adherence scale: medication compliance, collaboration with health care providers, willingness to access and use information on medication, and acceptance to take medication. Logistic regression analysis was performed to assess the correlation between the level of each medication adherence domain and each personality trait. The data of 128 patients with cardiovascular disease were analyzed. Higher conscientiousness score was significantly associated with a high compliance score (odds ratio per 1 point increase, 1.90; 95% confidence interval, 1.30-2.79; p = 0.001), high collaboration score (1.90; 1.31-2.76; p = 0.001), and high willingness score (1.74; 1.19-2.54; p = 0.004) after adjustment for potential confounders. Other combinations of personality traits and medication adherence showed no statistically significant correlations in multivariate analyses. The findings of this study suggest that assessment of personality traits, especially conscientiousness, may facilitate patient-medical staff communication for the improvement of medication adherence in patients with cardiovascular disease.
Copyright: © 2022 Adachi et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Ambrosetti M, Abreu A, Corrà U, Davos CH, Hansen D, Frederix I, et al.. Secondary prevention through comprehensive cardiovascular rehabilitation: From knowledge to implementation. 2020 update. A position paper from the Secondary Prevention and Rehabilitation Section of the European Association of Preventive Cardiology. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2021;28: 460–495. doi: 10.1177/2047487320913379 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources