Antheraea peptide and its analog: Their influence on the maturation of the reproductive system, embryogenesis, and early larval development in Tenebrio molitor L. beetle
- PMID: 36454989
- PMCID: PMC9714928
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0278473
Antheraea peptide and its analog: Their influence on the maturation of the reproductive system, embryogenesis, and early larval development in Tenebrio molitor L. beetle
Abstract
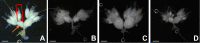
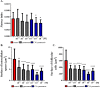
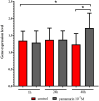
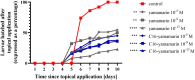
In recent years, many new immunologically active peptides from insects have been identified. Unfortunately, in most cases, their physiological functions are not fully known. One example is yamamarin, a pentapeptide isolated from the caterpillars of the Antheraea yamamai moth. This peptide has strong antiproliferative properties and is probably involved in the regulation of diapause. Additionally, antiviral activity was discovered. The results of the research presented in this paper are, to our knowledge, the first attempt to characterize the biological effects of yamamarin on the functioning of the reproductive processes and embryonic development of insects using a model species, the beetle Tenebrio molitor, a commonly known pest of grain storage. Simultaneously, we tested the possible activity of the molecule in an in vivo system. In this research, we present the multifaceted effects of yamamarin in this beetle. We show that yamamarin influences ovarian growth and development, maturation of terminal oocytes, level of vitellogenin gene transcript, the number of laid eggs, duration of embryonic development, and larval hatching. In experiments with palmitic acid-conjugated yamamarin (C16-yamamarin), we also showed that this peptide is a useful starting molecule for the synthesis of biopharmaceuticals or new peptidomimetics with gonadotropic activity and effects on embryonic development. The data obtained additionally provide new knowledge about the possible function of yamamarin in insect physiology, pointing to the important role of this pentapeptide as a regulator of reproductive processes and embryonic development in a heterologous bioassay with T. molitor.
Copyright: © 2022 Walkowiak-Nowicka et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures






References
-
- Yang P, Abe S, Zhao Y-p, An Y, Suzuki K. Growth suppression of rat hepatoma cells by a pentapeptide from Antheraea yamamai. J Insect Biotechnol Sericol. 2004;73(1):7–13. doi: 10.11416/jibs.73.7 - DOI
-
- Yang P, Abe S, Sato Y, Yamashita T, Matsuda F, Hamayasu T, et al.. A palmitonyl conjugate of an insect pentapeptide causes growth arrest in mammalian cells and mimics the action of diapause hormone. Journal of Insect Biotechnology and Sericology. 2007;76(2):63–69. doi: 10.11416/jibs.76.2_63 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

